How AI Agents and Agentic AI Are Transforming Tech
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has changed a lot over the years. In the beginning, AI was just about following simple commands, like setting reminders or giving weather updates. But now, AI systems have become more powerful and smarter. They can handle complex tasks, make decisions, and work in smarter ways. This change brings up two important ideas: AI agents and Agentic AI. Even though they sound alike, they are very different. Understanding these two terms is key to knowing how future intelligent systems will work and impact the world around us.
In this post, we’ll explain what sets AI agents and Agentic AI apart and why it matters.
What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are computer programs that can work on their own to complete specific tasks. They follow instructions, make decisions based on the information they get, and deliver results. These agents are often designed for repetitive or well-defined tasks, which makes them reliable helpers in various industries.
How Do AI Agents Work?
AI agents follow a simple three-step process:
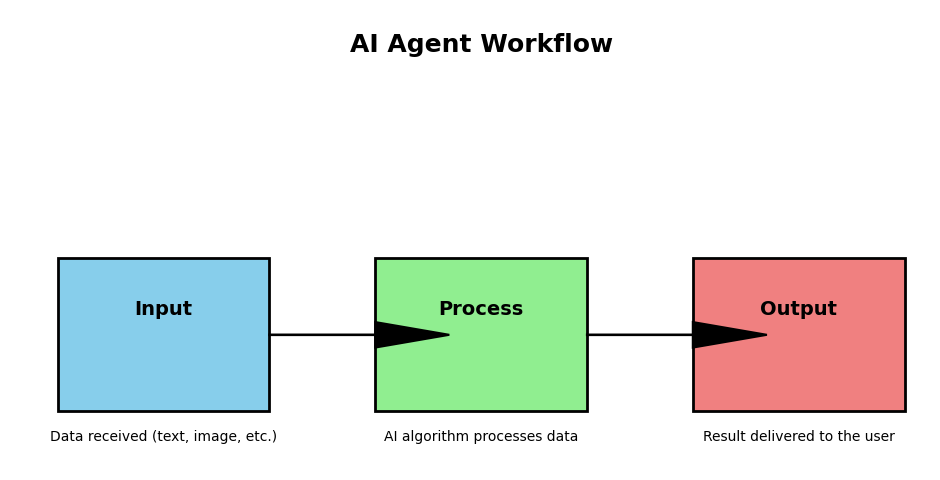
- Input: They receive information or a request.
- Example: A chatbot gets a question like “What’s the weather today?”
- Process: The agent analyzes the information and finds the best response or action.
- Example: The chatbot searches for weather data from a trusted source.
- Output: The agent provides a solution or completes an action.
- Example: The chatbot responds, “Today’s weather is sunny with a high of 75°F.”
This flow—Input → Process → Output—is what makes AI agents reliable for handling tasks without needing constant human involvement.
Real-Life Examples of AI Agents
- Chatbots for Customer Service:
AI-powered chatbots, like ChatGPT, handle customer questions on websites or messaging apps. They provide instant responses and reduce the need for human support. - Robotic Process Automation (RPA):
RPA tools automate repetitive tasks in businesses, such as filling out forms, sending emails, or processing data. This saves time and minimizes errors.
Strengths of AI Agents
- Fast and Efficient: They can process tasks much faster than humans.
- Consistent Performance: They don’t get tired or make mistakes from fatigue.
- Cost-Saving: Companies can reduce operational costs by automating routine tasks.
Limitations of AI Agents
- Limited Understanding: AI agents work well when the task is clearly defined but struggle with problems that require creativity or complex decision-making.
- Adaptability Issues: If the task changes or becomes too complicated, the agent may not know what to do.
- Dependency on Data: They need accurate and high-quality data to function correctly.
Must Read
- Monotonic Sequence in Python: 7 Practical Methods With Edge Cases, Interview Tips, and Performance Analysis
- How to Check if Dictionary Values Are Sorted in Python
- Check If a Tuple Is Sorted in Python — 5 Methods Explained
- How to Check If a List Is Sorted in Python (Without Using sort()) – 5 Efficient Methods
- How Python Searches Data: Linear Search, Binary Search, and Hash Lookup Explained
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI is a smarter type of AI that can make its own decisions, learn from experiences, and handle tasks without being told exactly what to do. Unlike regular AI that needs clear instructions, this advanced AI can figure things out and even solve new problems by itself.
How Does Agentic AI Work?
Here are five simple ways Agentic AI works:
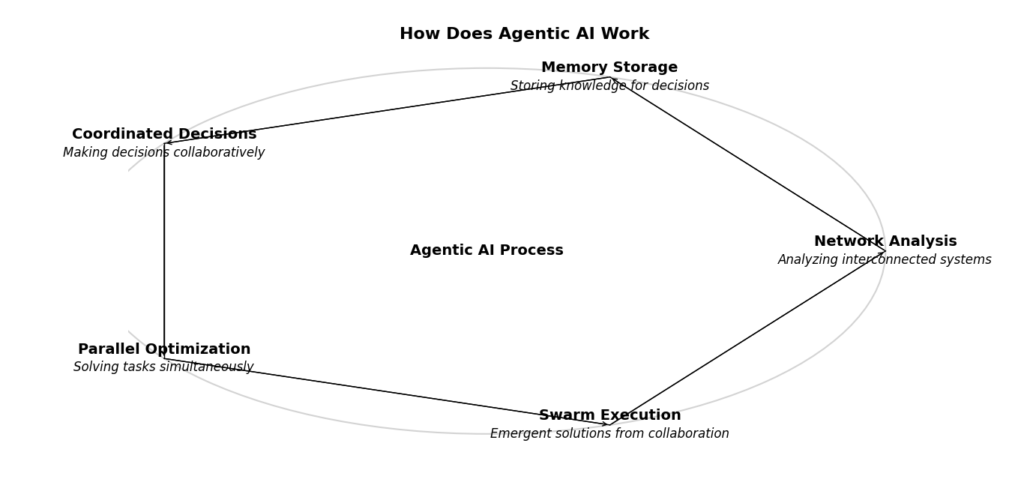
- Understanding Connected Systems (Network Analysis)
- It notices how things are linked and makes smart decisions based on those connections.
- Example: If one delivery truck breaks down, it finds another way to get your package to you.
- Remembering Information (Memory Storage)
- It remembers past experiences to make better decisions in the future.
- Example: A robot in a warehouse remembers which path is the fastest to reach certain shelves.
- Making Smart Choices Together (Coordinated Decision-Making)
- Different AI systems talk to each other and work together to solve problems.
- Example: Drones and trucks share traffic information to pick the fastest delivery routes.
- Solving Multiple Tasks at Once (Parallel Optimization)
- It does many tasks at the same time to get things done faster.
- Example: A smart system can pack orders, send delivery notifications, and schedule drivers all at once.
- Teamwork Among AI Systems (Swarm Execution)
- Many AI systems work together like a team to solve big problems.
- Example: A group of cleaning robots working together to clean a large shopping mall.
Real-Life Examples of Agentic AI
- Smart Factories: Machines that adjust production based on demand and available supplies without human input.
- Autonomous Delivery Fleets: Driverless trucks and drones that work together to deliver packages faster.
Why Is Agentic AI Important?
Agentic AI is special because it can learn and improve over time. It doesn’t just follow rules—it gets smarter as it handles more tasks. This makes it perfect for dealing with big, messy problems in industries like logistics, healthcare, and manufacturing.
Key Differences Between AI Agents and Agentic AI
| Feature | AI Agents | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| What It Is | AI that follows instructions to complete simple tasks | Advanced AI that thinks, learns, and adapts on its own |
| How Smart? | Follows rules but doesn’t learn | Learns from experience and gets better over time |
| Independence | Needs humans to give instructions | Can work without constant human help |
| Task Type | Good for simple, predictable tasks | Handles big, complex, and changing problems |
| Memory | Doesn’t remember past tasks | Remembers and uses past experiences to improve |
| Working Together | Usually works alone | Works as a team with other AI systems |
| Real-Life Examples | Chatbots that answer customer questions | Self-driving cars that learn better routes |
| Why It’s Useful? | Helps with routine, repetitive tasks | Can solve complex problems and adapt to new situations |
AI agents are great for simple jobs like answering questions or scheduling tasks. Agentic AI goes beyond that—it can think for itself, learn new things, and handle more complex challenges.
Real-World Applications
AI Agents Applications
These are systems designed to handle specific tasks based on clear instructions:
AI Agents (Task-Focused Helpers)
These are AI systems that follow clear instructions to complete specific tasks.
- Customer Support Chatbots:
- When you visit a website and ask questions like “Where’s my order?” a chatbot (like ChatGPT) gives you answers.
- How it works: It picks the best response from a list of pre-written answers.
- Email Sorting:
- AI helps organize your inbox by moving emails to different folders, marking spam, or tagging important ones.
- Example: Gmail automatically sends promotional emails to a “Promotions” tab to keep your inbox clean.
Agentic AI (Independent Problem-Solvers)
This is next-level AI that makes decisions, learns from experiences, and adapts on its own.
- Healthcare Diagnostics:
- AI looks at patient records from different hospitals to suggest better treatments.
- Example: AI detecting early signs of diseases like cancer by comparing thousands of patient records.
- Financial Trading Systems:
- AI watches stock markets and makes trading decisions without waiting for human input.
- Example: Buying and selling stocks instantly to get the best profits based on live market changes.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
AI Agents: Challenges
- Limited Creativity and Adaptability:
- AI agents can only do what they are programmed to do. They cannot think outside the box or adjust to new situations in creative ways.
- Example: A chatbot can only answer questions that match the ones it was trained on. It can’t adapt to totally new, unplanned questions.
- Reliance on Rule-Based Systems:
- These AI systems follow strict rules, meaning if something unexpected happens, they might not know how to respond.
- Example: If an email sorting AI sees a new kind of spam message, it may not recognize it and could accidentally send it to your inbox.
Agentic AI: Challenges
- Potential for Unintended Consequences:
- Because Agentic AI learns on its own and can make decisions, it might sometimes take actions that weren’t expected or planned.
- Example: An AI used in trading might sell all your stocks at once because it learned that rapid changes can make the most profit—but this might not always be a good decision.
- Ethical Concerns Around Autonomy and Decision-Making:
- Agentic AI can make decisions without human input, raising questions about whether it should have that much power. Who is responsible if the AI makes a harmful decision?
- Example: Should an autonomous car decide how to react in a crash situation, or should a human still be in charge?
Shared Ethical Concerns (Both AI Agents and Agentic AI)
- Data Privacy and Security:
- Both types of AI need to collect and use large amounts of data, which can sometimes include personal information. This raises concerns about who has access to that data and how it’s protected.
- Example: AI systems storing personal information from customer service interactions might get hacked, exposing sensitive data.
The Future of Intelligent Systems
As AI continues to grow, we’re moving toward hybrid models that combine the strengths of both AI Agents and Agentic AI. By blending their unique abilities, these hybrid systems can offer better efficiency while maintaining the flexibility to adapt to new challenges. Let’s break down what this future could look like.
Integration of AI Agents and Agentic AI
Imagine combining the predictable, task-specific strengths of AI agents with the adaptive, learning abilities of Agentic AI. This balance can lead to smarter systems that can handle both routine tasks and complex, ever-changing situations.
- Hybrid Models:
These systems can perform repetitive tasks quickly and efficiently, like AI agents, while also making smarter decisions when the situation calls for it, like Agentic AI.- Example: A factory robot that can assemble parts quickly (AI Agent) but also adjusts its process when something unexpected happens (Agentic AI).
The Road Ahead: Key Developments
- Advancements in Memory and Reasoning Systems:
In the future, AI systems will be able to remember past actions and make decisions based on reasoning. This will allow them to handle even more complex scenarios.- Example: AI that can remember your preferences over time and offer personalized recommendations.
- Increased Ethical Oversight:
As AI gets smarter, we will need stronger ethics and accountability to ensure these systems make decisions in ways that are fair and safe.- Example: Having guidelines in place to ensure AI systems used in healthcare always prioritize patient safety and privacy.
Conclusion
AI is changing fast. We’re moving from systems that only do specific tasks (AI Agents) to smarter systems that can think, learn, and solve problems on their own (Agentic AI).
In the future, combining these two types of AI will help create better solutions that are both efficient and adaptable. Understanding this difference is important for anyone working with AI or building AI-powered products.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between AI Agents and Agentic AI?
2. Can AI Agents and Agentic AI work together?
3. Why is understanding Agentic AI important?
4. What are some ethical concerns with Agentic AI?
External Resources
Understanding AI Agents and Their Applications
AI Agent Systems and Use Cases – A detailed overview of AI agents and how they are shaping industries.
Ethical Concerns in Advanced AI Systems
Ethics of Autonomous AI – An in-depth discussion on the ethical challenges of advanced AI technologies.
Hybrid AI Systems in Business
Combining AI Agents with Agentic AI for Smarter Solutions – Real-life examples of hybrid AI models driving innovation.
The Future of AI
Emerging Trends in AI – Predictions and expert opinions on the evolution of intelligent systems.




Leave a Reply