How to Swap Two Variables Without Using a Third in Python – Explained
Introduction
Swapping two variables is something you’ll do often in programming. Maybe you’re sorting numbers, swapping player turns in a game, or just switching values for some logic to work.
The traditional way to swap two variables is by using a third (temporary) variable. You store one value in the temporary variable, move the second value to the first, and then assign the stored value back to the second. It works, but there’s a cleaner way!
In Python, you can swap two variables without needing a third one. This method is not only shorter but also makes your code easier to read and understand. Plus, Python’s way of swapping is optimized, so it can be slightly faster than the traditional approach in some cases.
Let’s see how it works!
Why Swap Two Variables Without a Temporary Variable?

Skipping the extra variable might seem like a small thing, but it comes with real benefits:
- Saves memory space – You don’t need an extra variable, which can be useful when working with limited memory.
- Keeps the code clean – The swap happens in a single line, making it easier to read and understand.
- Uses Python’s built-in features – Python allows swapping with tuple unpacking, which is both elegant and efficient.
- Great for interviews and coding challenges – Many coding interviews test how well you can simplify logic, and this trick shows you know how to write smart, efficient code.
Now, let’s see how it works in action!
Traditional Method: Swapping with a Temporary Variable
One of the most common ways to swap two variables is by using a temporary variable. Here’s how it works:
Code Example
a = 5
b = 10
temp = a # Store the value of 'a' in a temporary variable
a = b # Assign the value of 'b' to 'a'
b = temp # Assign the stored value (original 'a') to 'b'
print(a, b) # Output: 10 5
Step-by-Step Explanation
- Store the first variable (
a) in a temporary variable (temp)temp = a→ Now,tempholds the value5.
- Assign the value of the second variable (
b) to the first variable (a)a = b→ Now,abecomes10.
- Assign the value stored in
temp(which was the originala) tobb = temp→ Now,bbecomes5.
After these steps, the values of a and b are successfully swapped!
Why This Works
By temporarily holding the value of a, we don’t lose it when we overwrite a with b. This ensures that b can then safely take the stored value of a.
Downside of This Approach
- Uses extra memory – The temporary variable
temptakes up additional space in memory. - More lines of code – Although simple, this method is not the most concise way to swap variables in Python.
Python offers a cleaner and more efficient way to swap variables without needing a temporary variable. Let’s check that out next!
Must Read
- Monotonic Sequence in Python: 7 Practical Methods With Edge Cases, Interview Tips, and Performance Analysis
- How to Check if Dictionary Values Are Sorted in Python
- Check If a Tuple Is Sorted in Python — 5 Methods Explained
- How to Check If a List Is Sorted in Python (Without Using sort()) – 5 Efficient Methods
- How Python Searches Data: Linear Search, Binary Search, and Hash Lookup Explained
Pythonic Way: Swap Two Variables Without a Third
Python gives us a simple and elegant way to swap two variables without needing an extra variable. This method uses tuple unpacking, which makes the swap cleaner and more efficient.
1. Using Tuple Unpacking (Recommended)
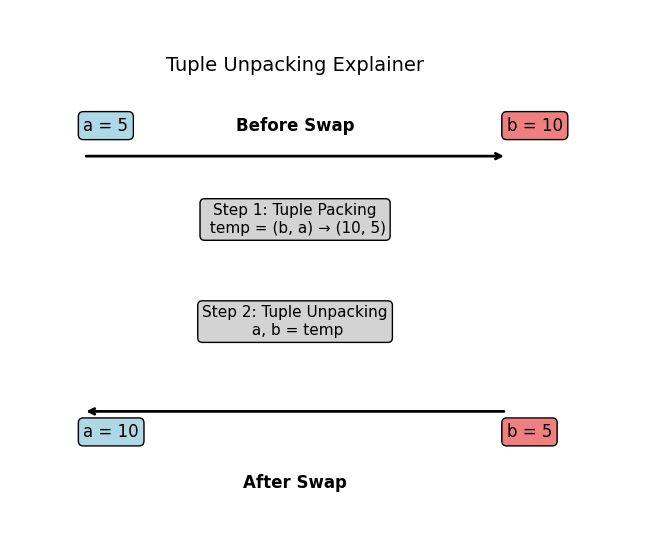
Code Example
a = 5
b = 10
a, b = b, a # Swap values in one line
print(a, b) # Output: 10 5
How This Works
Python evaluates the right-hand side (b, a) first as a tuple (10, 5), then unpacks these values directly into a and b.
Step-by-Step Execution:
b, acreates a temporary tuple(10, 5).- Python unpacks
10intoaand5intob. - The values are swapped in a single step, without needing an explicit temporary variable.
Why This Method is Better
- No extra memory used – No need for a temporary variable.
- One-liner code – Short and easy to read.
- More efficient – Python internally optimizes this swapping process.
- Looks clean – The code is self-explanatory, making it great for readability.
This method is widely used in competitive programming, interviews, and everyday coding because it’s simple and efficient. Now, let’s explore some other interesting ways to swap variables in Python!
2. Using Arithmetic Operations
Another way to swap two variables without using a third variable is through arithmetic operations. One of the most common methods is addition and subtraction.
Method 1: Using Addition and Subtraction
Code Example
a = 5
b = 10
a = a + b # a = 15 (5 + 10)
b = a - b # b = 5 (15 - 10)
a = a - b # a = 10 (15 - 5)
print(a, b) # Output: 10 5
How This Works
a = a + b→abecomes5 + 10 = 15.b = a - b→bbecomes15 - 10 = 5(originalavalue).a = a - b→abecomes15 - 5 = 10(originalbvalue).
Now, the values of a and b are successfully swapped without needing an extra variable.
Benefits
- No extra memory used – No need for a temporary variable.
- Slightly faster in some cases – Arithmetic operations are low-level operations, which can be quicker in certain scenarios.
Downside
- Integer Overflow Risk – In languages with fixed integer sizes (like C, Java), very large numbers can cause an overflow. However, Python handles large integers dynamically, so this is not an issue in Python.
While this method works well, the tuple unpacking method (a, b = b, a) is still the preferred choice in Python because it’s more readable and optimized.
Let’s look at another interesting approach using bitwise XOR!
Method 2: Using XOR Bitwise Operator
Another way to swap two variables without extra memory is by using the XOR (Exclusive OR) bitwise operator. This method is often used in low-level programming and embedded systems because it directly manipulates bits.
Code Example
a = 5
b = 10
a = a ^ b # Step 1: a = 5 ^ 10
b = a ^ b # Step 2: b = (5 ^ 10) ^ 10 → b = 5
a = a ^ b # Step 3: a = (5 ^ 10) ^ 5 → a = 10
print(a, b) # Output: 10 5
How This Works (Bitwise Breakdown)

The XOR (^) operator compares corresponding bits of two numbers:
- If the bits are different, the result is
1. - If the bits are the same, the result is
0.
Let’s see how this works for a = 5 and b = 10:
Step 1: Compute a = a ^ b
Binary representation:
5 → 0101
10 → 1010
----------------
XOR → 1111 (Now, `a = 15`)
Step 2: Compute b = a ^ b
15 → 1111
10 → 1010
----------------
XOR → 0101 (Now, `b = 5`)
Step 3: Compute a = a ^ b
15 → 1111
5 → 0101
----------------
XOR → 1010 (Now, `a = 10`)
Benefits
- Works at the bit level – Makes it useful for low-level programming (e.g., embedded systems, cryptography).
- No extra memory used – The swap happens within the same variables.
Downside
- Less readable for beginners – Bitwise operations can be harder to understand than tuple unpacking (
a, b = b, a). - Not always faster – Modern Python optimizations make tuple unpacking the best choice for readability and performance.
Even though this method is clever, tuple unpacking remains the best choice for most Python programs because it’s simple, readable, and optimized.
Let’s wrap things up with a final comparison of these methods!
Which Method is Best?
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Tuple Unpacking | Readable, Fast, No extra memory | None (Best for Python) |
| Addition/Subtraction | Simple, No extra variable | Risk of overflow |
| XOR Bitwise Operator | Works at low level, No extra memory | Harder to understand, Bitwise logic needed |
When to Use These Swapping Methods?
Each method has its ideal use case, depending on the programming language and scenario:
| Method | When to Use It |
|---|---|
Tuple Unpacking (a, b = b, a) | ✅ Best for Python – Readable, memory-efficient, and optimized. Use it in all Python programs. |
Arithmetic Operations (+ and -) | ✅ Useful for interviews – Helps demonstrate problem-solving skills. Also relevant in languages without built-in swap features. |
Bitwise XOR (^) | ✅ Ideal for low-level bit manipulation – Useful in embedded systems, cryptography, and hardware-level programming. |
For Python developers, tuple unpacking is the best and most recommended method. If you’re coding in other languages, addition/subtraction or XOR swapping may be more useful, depending on the situation.
Conclusion
Swapping two variables without using a third is a simple yet essential trick in programming. In Python, the best approach is tuple unpacking (a, b = b, a), which is clean, efficient, and easy to understand.
For those preparing for coding interviews, knowing arithmetic-based swapping can be useful, especially in languages with stricter memory constraints. Meanwhile, bitwise XOR swapping is a clever technique often used in low-level programming and embedded systems.
If you’re writing Python code, stick to tuple unpacking—it’s the simplest, most readable, and optimized solution. But if you’re exploring different programming paradigms, understanding arithmetic and bitwise approaches can expand your problem-solving skills.
Want to master more Python tricks? Stay tuned for more insightful guides on Emitech Logic!
FAQs on Swapping Two Variables Without a Third in Python
1. Why is tuple unpacking (a, b = b, a) the best method for swapping in Python?
2. Can I use addition/subtraction for swapping in all programming languages?
3. When should I use XOR swapping instead of tuple unpacking?
4. Is there any performance difference between these swapping methods?
External Resources
If you want to explore more about variable swapping and Python tricks, check out these helpful resources:
- Python Official Documentation – Data Structures
Learn about Python’s built-in data structures, including tuples, which make swapping variables so efficient. - GeeksforGeeks – Swapping Two Numbers in Python
A detailed explanation of different swapping methods with examples and performance comparisons. - Python Bytes – Common Interview Questions in Python
A podcast covering Python tips, tricks, and best practices for coding interviews.
These resources will help you deepen your understanding of Python swapping techniques and improve your coding skills.






Leave a Reply