Building an AI-Powered Tutor with RAG and Vector Databases
Introduction: The Future of Personalized Learning
The Rise of AI in Education
A few years ago, most classrooms looked the same: one teacher, thirty students, one pace for everyone. Some kids raced ahead and got bored. Others fell behind and felt lost. It wasn’t anyone’s fault—it’s just hard for one person to teach thirty different minds at once.
Now picture this: a quiet helper that sits next to every single student. This helper knows exactly where you are strong, where you get stuck, and what kind of explanation clicks for you. If you learn best with pictures, it draws them. If you like stories, it tells one. If you need to try ten examples, it patiently gives you ten more.
That helper is artificial intelligence. It’s already happening in small ways—apps that adjust math problems to your level, language programs that listen to your pronunciation and fix it gently. AI doesn’t get tired, doesn’t judge, and can spend as much time as you need. For the first time in history, truly personal teaching isn’t just for princes and princesses with private tutors—it can be for everyone.
Limitations of General Purpose LLMs for Tutoring
Now, the most famous AI tools today—like the big chat models everyone talks about—are amazingly clever. They can write poems, explain physics, even crack jokes. But when it comes to being a real tutor, they often stumble.
Here’s why. These models learned by reading huge amounts of text from the internet—books, websites, forums, everything. They’re like a student who read a thousand textbooks overnight but never checked which parts were correct or up-to-date.
So when you ask a deep question about, say, quantum mechanics or advanced biology, they sometimes mix things up. They might confidently give an answer that sounds perfect but is actually outdated or slightly wrong. Or they might make up facts that aren’t in any book—this is called “hallucinating.”
Even worse, they don’t really remember what they told you five minutes ago in a long conversation. They can repeat general ideas, but they struggle to stay perfectly accurate on specific topics, especially if the topic needs the latest research or very precise details.
In short: they’re brilliant conversationalists, but not yet trustworthy teachers for serious subjects.
Introducing RAG: The Solution for Accurate AI Tutors
This is where our story gets interesting. A few smart people asked: “What if we didn’t let the AI guess from memory alone? What if we gave it a library card?”
That idea became Retrieval-Augmented Generation, or RAG for short.
Here’s how it works—think of it like this:
You’re the student asking a question. The AI doesn’t try to answer straight from its head. Instead, it first goes to a special, carefully chosen library (a collection of trusted documents—textbooks, research papers, lecture notes—whatever the subject needs). It quickly searches that library, finds the most relevant pages, and reads them. Only then does it write the answer—using exactly what it just read as its source.
It’s like having a tutor who, every time you ask something, pulls out the right textbook, finds the exact paragraph, and explains it in simple words. No guessing, no making things up. The answer stays grounded in real, verified information.
Because the library is chosen by humans who know the subject, the AI suddenly becomes much more accurate and reliable. It still speaks naturally and patiently, but now it’s standing on solid ground.
What You Will Learn: Blog Post Outline Overview
By the end of this journey together (the full blog post), you’ll know how to build one of these smart tutors yourself.
We’ll walk step by step through:
- How to take good educational material (PDFs, notes, textbooks) and turn it into a form the computer can search quickly.
- How to store all that knowledge in a special kind of database called a vector database—one that’s perfect for finding similar ideas, not just exact words.
- How to connect everything so that when a student asks a question, the system quietly finds the best pieces of knowledge and feeds them to a fast language model.
- How to add a simple, friendly interface (like a chat window) so anyone can talk to your tutor.
- And finally, how to put it online so others can use it.
You don’t need to be an expert to follow along—just curiosity and a little patience. We’ll use free or affordable tools, write clear code together, and test everything as we go.
When we’re done, you’ll have your own accurate, personalized AI tutor running on your computer—one that knows exactly the subject you choose and almost never makes things up.
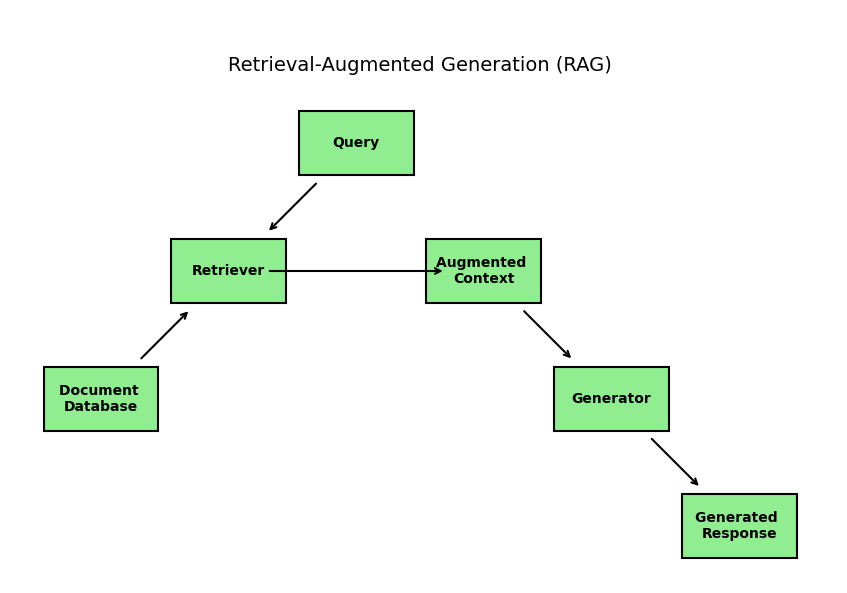
Understanding the Core Technologies Behind RAG-Based AI Tutors
Large Language Models (LLMs) in Tutoring Systems
The first worker is the one who does all the talking — we call it the Large Language Model, or LLM for short.
This is the same kind of brain that powers popular chat apps like Grok or others you know. It’s the part that reads your question and writes back in clear, natural sentences. It can explain concepts simply, give step-by-step examples, ask gentle questions to check your understanding, and even encourage you with “Great job!” when you get something right.
It’s the friendly, conversational voice of the AI-powered tutor — the one the student actually talks to every day.
But as we already saw earlier, this voice is very good at speaking beautifully… and sometimes a little too creative with facts. That’s why it needs help from the other workers. Alone, it’s charming but not always perfectly accurate for educational use.
The Power of Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
The second worker is the careful researcher — this is Retrieval-Augmented Generation, or RAG.
Every time a student asks a question, RAG steps in first. It doesn’t let the talking voice (the LLM) answer yet.
Instead, RAG quickly searches through our trusted collection of educational materials — textbooks, lecture notes, research papers, and reliable sources. It finds the most relevant sections, reads them, and hands those exact passages to the LLM with a quiet note: “Here are the verified facts. Use these to answer.”
Because of this simple but powerful hand-off, the final response stays honest, factual, and up-to-date. RAG is the key technology that makes AI tutors reliable and reduces hallucinations — it’s why modern RAG-based AI tutors in 2025 are so much better than basic LLMs for personalized education.
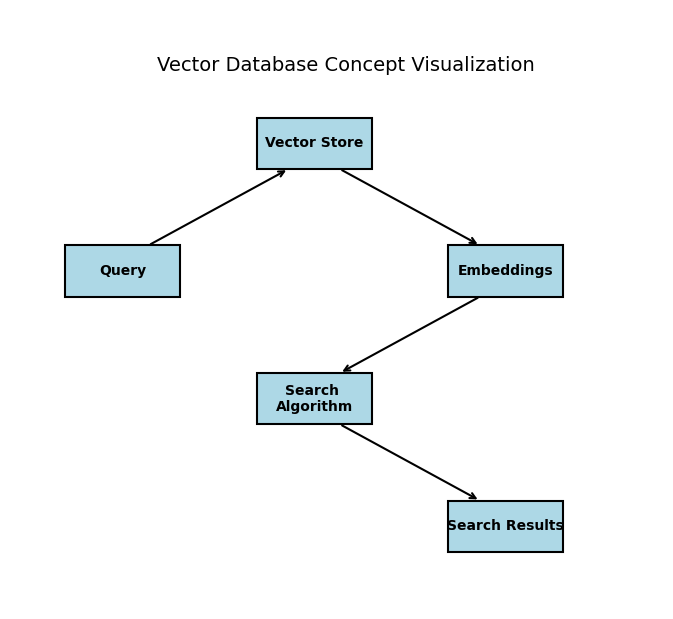
The Importance of Vector Databases for Semantic Search
The third worker is the super-fast librarian — the vector database.
Traditional databases store text like books on a shelf, searchable only by exact words or titles. But student questions are rarely that precise.
A vector database solves this by turning every paragraph, sentence, or section of your educational content into a numerical “fingerprint” called an embedding. These embeddings capture the meaning, not just the words — so similar ideas end up close together in a high-dimensional space.
When RAG needs relevant information, it converts the student’s question into an embedding too. The vector database instantly finds the closest matches — the paragraphs with the most similar meaning — and returns them in milliseconds.
This enables semantic search, making retrieval fast and accurate even with thousands of pages. Popular vector databases in 2025 include Pinecone, Weaviate, Chroma, and FAISS — they’re essential for any efficient RAG pipeline in AI tutoring systems.
D. Key Components of an AI Tutor Architecture Using RAG and Vector Databases
Now let’s stand back and see how these parts connect in our complete AI tutor architecture:
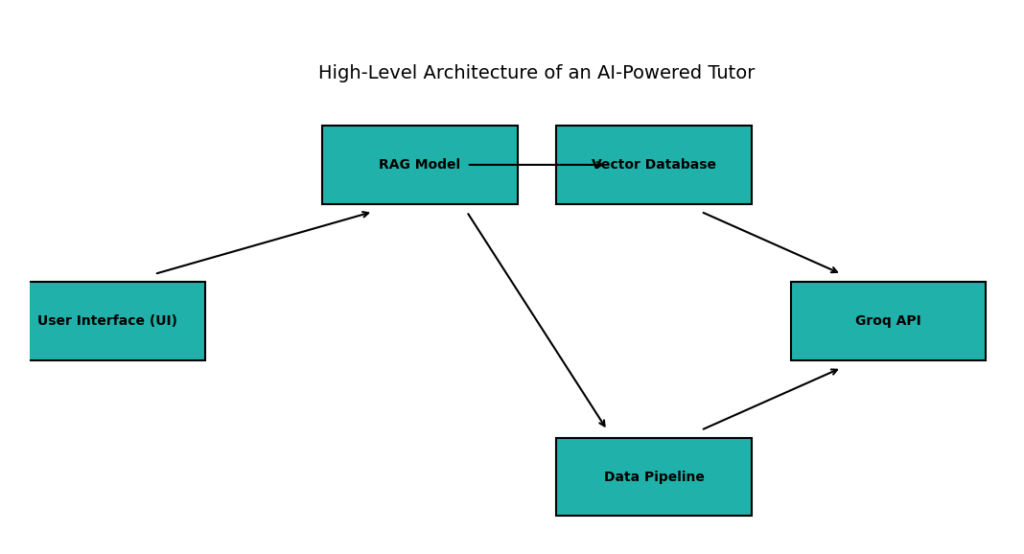
- The student interacts through a simple chat interface (the front door — often built with Streamlit or Gradio).
- The question flows to the RAG pipeline (the researcher).
- RAG queries the vector database (the librarian) for the most relevant knowledge chunks.
- The vector database returns the best matches quickly.
- RAG combines the original question with these retrieved passages and sends everything to the LLM (the talking voice).
- The LLM generates a clear, engaging, and accurate response using the grounded context.
- The answer returns to the student via the chat interface.
It’s a smooth, efficient loop. From the outside, it feels like one intelligent tutor. Behind the scenes, LLMs, RAG, and vector databases work together seamlessly to deliver personalized, trustworthy learning experiences.
The Responsive RAG Tutor Simulator
RAG TUTOR SIMULATOR
Vector DB & LLM Integration
Step 1: User Query
Step 2: AI Response
Waiting for input…
How to Use the RAG Simulator
This interactive tool demonstrates the three-step architecture of an AI-Powered Tutor. Follow these steps to see how Retrieval-Augmented Generation works in real-time:
- Enter a Query: Type a technical question into the input field (e.g., “What is a Vector Database?”).
- Observe the Retrieval: Watch the Progress Bar. The system first converts your text into a vector embedding to search the database for relevant context.
- Witness the Generation: The “Tutor Response” terminal will simulate the LLM (Large Language Model) synthesizing an answer that is specifically grounded in the retrieved data.
- Auto-Contained Results: The response is limited to the simulator terminal, ensuring a clean reading experience without shifting the page layout.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide for Your RAG-Based AI Tutor
Setting Up Your Development Environment
First, we need a clean workspace.
Create a new folder for the project and open it in your favorite code editor (VS Code works great).
We’ll use Python—make sure you have Python 3.10 or newer.
Create a virtual environment:
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # On Windows: venv\Scripts\activateNow install the key libraries we’ll need:
pip install langchain langchain-groq langchain-community pinecone-client streamlit python-dotenv sentence-transformers pypdfWhy these?
- LangChain: Our main framework—it ties everything together gently.
- langchain-groq: For fast access to powerful LLMs via Groq (blazing quick inference in 2025).
- pinecone-client: To connect to Pinecone, our managed vector database.
- streamlit: For a simple, friendly chat interface.
- sentence-transformers: Free open-source embeddings (we’ll use a strong 2025 model like BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5).
- pypdf: To load educational PDFs easily.
- python-dotenv: To keep API keys safe.
Get your free API keys:
- Sign up at groq.com → Create a Groq API key.
- Sign up at pinecone.io → Create a free starter index (serverless, perfect for learning).
Create a .env file in your folder:
GROQ_API_KEY=your_groq_key_here
PINECONE_API_KEY=your_pinecone_key_here
PINECONE_ENVIRONMENT=your_region (e.g., us-east-1)Ready? Our workspace is set.
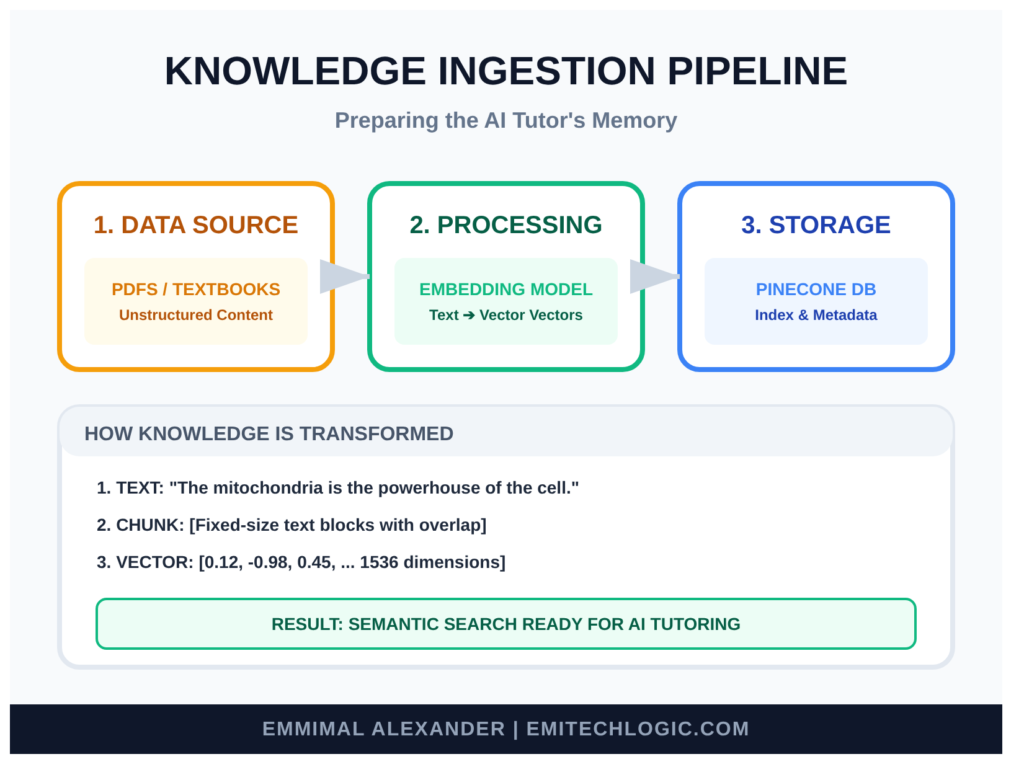
Preparing the Educational Data Knowledge Base
Our tutor needs good books to read from.
Choose a subject—let’s say “Introduction to Python Programming.” Gather trustworthy sources:
- Free textbooks (PDFs from official sites).
- Lecture notes.
- Reliable articles.
For this guide, download a few public-domain Python PDFs or use your own course materials.
We need to clean and split the text into manageable chunks (around 500-1000 characters each, with some overlap).
LangChain makes this gentle:
from langchain.document_loaders import PyPDFLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
loader = PyPDFLoader("your_python_textbook.pdf")
documents = loader.load()
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(
chunk_size=1000,
chunk_overlap=200
)
chunks = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
print(f"We now have {len(chunks)} clean chunks ready.")These chunks are the pages our librarian will store.
Creating Text Embeddings for RAG
Now we turn each chunk into that numerical fingerprint—an embedding.
In 2025, strong open-source options like BGE or Nomic Embed are excellent and free.
We’ll use BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5—fast, accurate, and perfect for English educational content.
from langchain.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
embedding_model = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(
model_name="BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5"
)
# Test one embedding
sample_embedding = embedding_model.embed_query("What is a variable in Python?")
print(f"Embedding length: {len(sample_embedding)}") # Usually 384 dimensionsThis runs locally—no cost, full privacy.
Storing and Indexing Vectors in a Vector Database
Here’s where we choose Pinecone—fully managed, serverless, and the top choice in 2025 for reliable RAG without any server worries.
First, create an index in your Pinecone dashboard (dimension matches your embedding model—384 for bge-small).
Here’s what the Pinecone dashboard looks like:
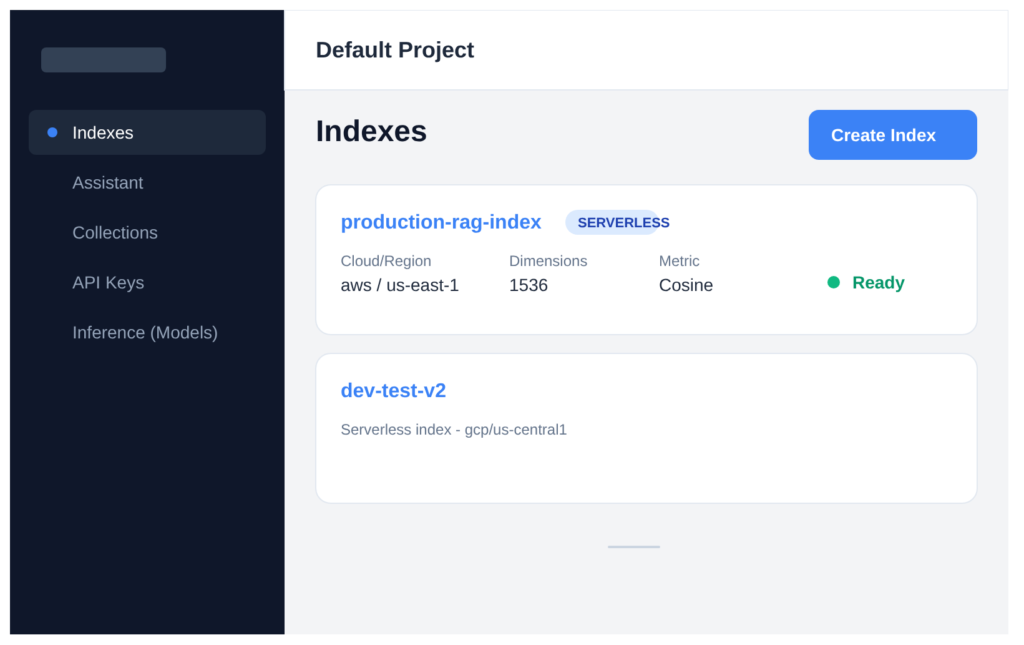
Now the code:
import os
from pinecone import Pinecone, ServerlessSpec
from langchain.vectorstores import Pinecone as LangchainPinecone
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
pc = Pinecone(api_key=os.getenv("PINECONE_API_KEY"))
index_name = "ai-tutor-index"
# Create index if it doesn't exist
if index_name not in pc.list_indexes().names():
pc.create_index(
name=index_name,
dimension=384, # Match bge-small
metric="cosine",
spec=ServerlessSpec(cloud="aws", region=os.getenv("PINECONE_ENVIRONMENT"))
)
# Connect and upsert
index = pc.Index(index_name)
vectorstore = LangchainPinecone.from_documents(
documents=chunks,
embedding=embedding_model,
index_name=index_name
)
print("All knowledge safely stored in Pinecone!")Your trusted library is now live and searchable.
Building the Retrieval Pipeline
This is the heart of RAG—finding the best pages before answering.
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever(
search_type="similarity",
search_kwargs={"k": 5} # Get top 5 most relevant chunks
)
# Test it
question = "How do loops work in Python?"
relevant_chunks = retriever.get_relevant_documents(question)
print("Found these helpful pages:")
for i, chunk in enumerate(relevant_chunks):
print(f"\n--- Chunk {i+1} ---\n{chunk.page_content[:300]}...")Fast and accurate—thanks to semantic search.
Configuring the LLM for Educational Responses
Finally, give our voice a gentle teaching style.
We’ll use Groq’s fast Llama 3.1 or Mixtral for quick, natural responses.
from langchain_groq import ChatGroq
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.schema.runnable import RunnablePassthrough
from langchain.schema.output_parser import StrOutputParser
llm = ChatGroq(
model_name="llama-3.1-70b-versatile", # Or mixtral-8x7b for speed
temperature=0.7
)
template = """You are a kind, patient tutor. Explain concepts clearly, step by step.
Use the following context to answer accurately:
Context: {context}
Question: {question}
Answer in a helpful, encouraging way."""
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template)
chain = (
{"context": retriever, "question": RunnablePassthrough()}
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
# Test
response = chain.invoke("Explain functions in Python with an example.")
print(response)Add a simple Streamlit chat interface:
Here’s how the final chat will feel:
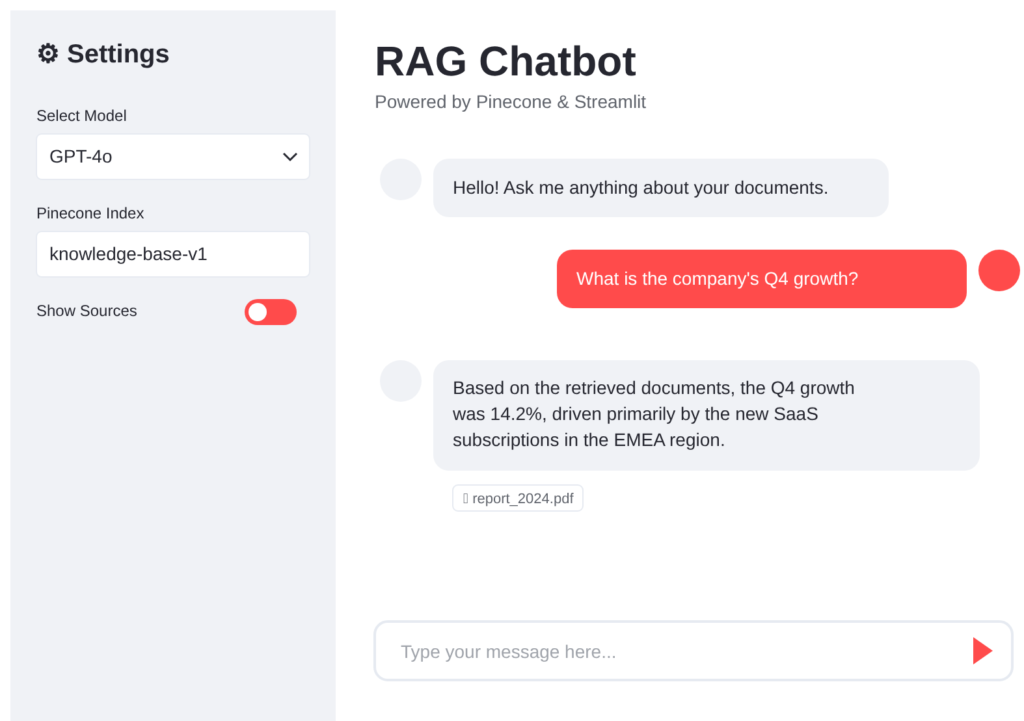
Create app.py:
import streamlit as st
# ... (imports from above)
st.title("Your Personal AI Tutor")
if "messages" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.messages = []
for message in st.session_state.messages:
with st.chat_message(message["role"]):
st.markdown(message["content"])
if prompt := st.chat_input("Ask me anything about the subject!"):
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": prompt})
with st.chat_message("user"):
st.markdown(prompt)
with st.chat_message("assistant"):
response = chain.stream(prompt)
full_response = st.write_stream(response)
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": full_response})This will open a web interface where you can type in questions and get answers from your AI-powered tutor.
Run with streamlit run app.py.
All code snippets above are from the full project.
Get the complete repository here: https://github.com/Emmimal/ai-powered-tutor-rag-vector-db/
There it is—your own accurate, patient AI-powered tutor with RAG and vector databases running in 2025.
Testing, Optimization, and Deployment of Your RAG-Based AI Tutor
Evaluating AI Tutor Performance and Accuracy
A good tutor doesn’t just talk—it teaches correctly.
We need quiet ways to measure if our RAG system is retrieving the right pages and if the final answers are accurate, clear, and helpful.
Here are some common, practical checks used in 2025:
- Retrieval metrics: How often do the top retrieved chunks actually contain the needed information? (Hit rate, Mean Reciprocal Rank)
- Answer metrics: Faithfulness (does the answer stick to the retrieved context?), Relevance, and Correctness (compared to ground-truth answers).
- Tools like Ragas or TruLens make this gentle—they run a set of test questions automatically and give you scores.
A simple evaluation cycle looks like this:
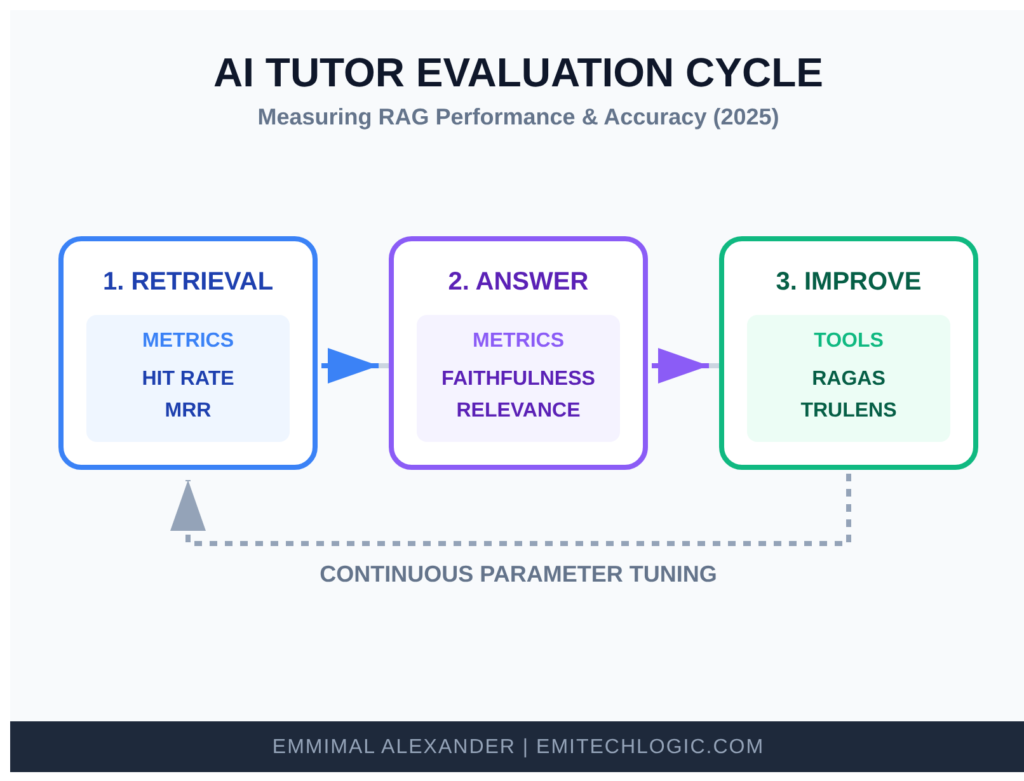
Start with 20–50 good test questions you know the answers to. Run them through your tutor. Look at the scores. If retrieval is low, try better chunking or a stronger embedding model. If answers drift, tighten your prompt.
Keep testing as you grow the knowledge base—this keeps trust high.
User Experience (UX) in AI Tutoring Platforms
The front door matters as much as what’s inside.
Students should feel safe, seen, and excited to knock.
Some gentle design ideas for your AI tutoring platform:
- Clean, calm colors and plenty of space.
- A warm greeting when they arrive: “Hi! I’m here to help with Python today. What would you like to learn?”
- Show progress: “You’ve mastered variables—let’s try functions next.”
- Easy ways to say “explain simpler” or “give me an example.”
- Dark/light mode, readable fonts, mobile-friendly.
Small touches—like showing retrieved sources or adding emojis—make learning feel human.
Deploying Your AI-Powered Tutor
Your tutor is ready to leave home and help more students.
In 2025, deployment is easier than ever. Here are reliable options:
- Streamlit Community Cloud (now part of Snowflake): Free tier, one-click deploy from GitHub.
- Hugging Face Spaces: Great for sharing with the community—free GPU options available.
- Vercel or Render: Fast for Streamlit apps.
- AWS/EC2 or Google Cloud Run: More control and scaling for larger use.
Typical deployment flow:
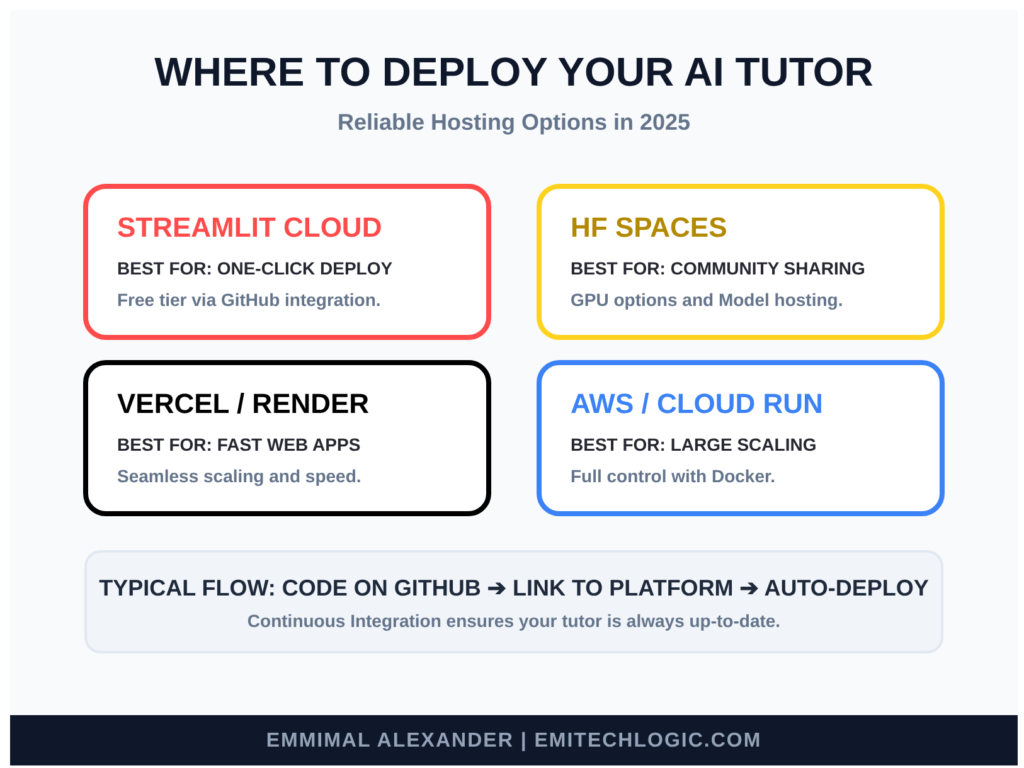
Push your code to GitHub → connect to the platform → add your secrets (API keys) → deploy. In minutes, you have a public URL.
Start private (share the link only with your students), then open it wider when ready.
Continuous Improvement Through Feedback Loops
The best tutors never stop learning themselves.
Build a gentle cycle:
- Let students give thumbs up/down on answers.
- Quietly log questions and responses (with privacy in mind).
- Once a month, review weak spots—add better sources, fix chunks, update embeddings.
- Retrain nothing heavy—just add new documents to your vector database.
Over time, your tutor grows wiser, more accurate, and more loved.
And there we are—the house is built, tested, welcoming, and standing openly for students to visit. It will keep getting better with every conversation.
You’ve walked the whole path now: from dreaming about personalized learning to holding a real, working AI-powered tutor with RAG and vector databases in your hands.
If a student somewhere learns something new because of what you built today, that’s the quiet magic of it all.
Ethical Considerations and Future Trends in AI Tutoring
Responsible AI in Education
Any tool that touches learning touches something sacred.
When we bring AI into education, we must handle it with steady hands.
Here are some of the gentle but firm promises we should keep:
- Bias: The books we put in our knowledge base come from humans, and humans carry quiet prejudices. If our sources favor one way of explaining things, or leave out certain voices, the tutor might repeat those patterns. Always choose diverse, balanced materials and check answers for fairness.
- Privacy: Students often share where they struggle. That information is private. Store as little as possible, never sell data, and use local or secure systems when you can. Be clear with students about what is saved and why.
- Transparency: Let students know they’re talking to an AI built on specific sources. Show the pages it used when possible. This builds trust and teaches them to question gently.
- Human role: An AI tutor is a helper, not a replacement for teachers, mentors, or friends. It should encourage curiosity, not shortcuts.
These ideas matter deeply in responsible AI in education:
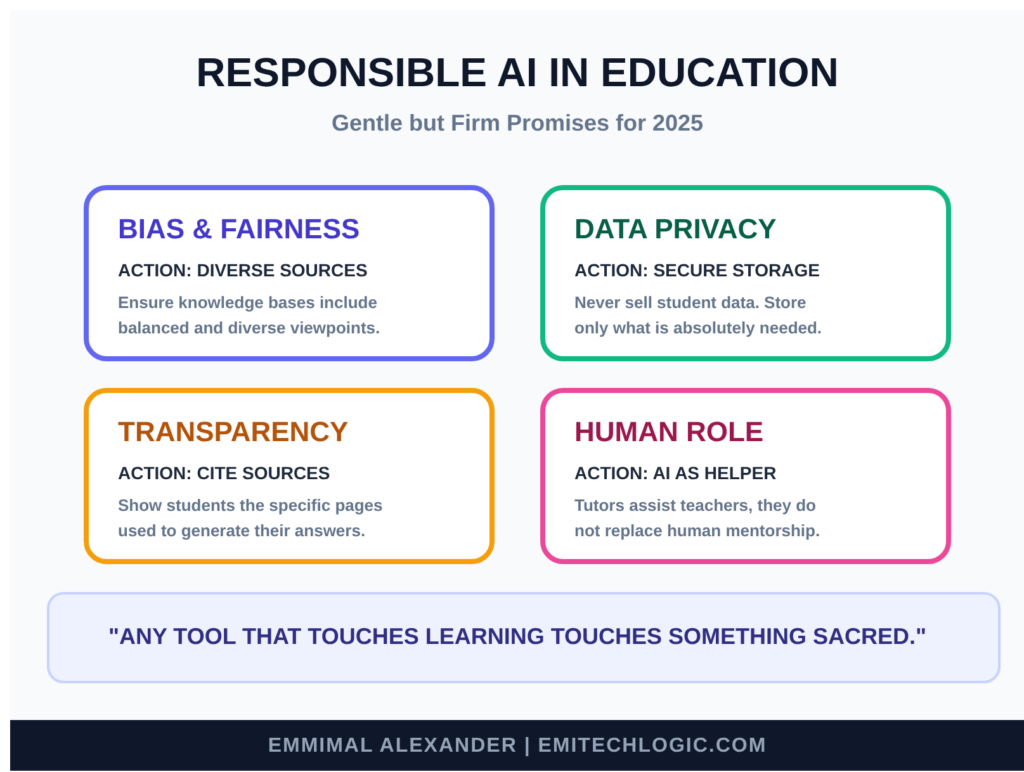
The Future of AI Tutoring Systems
Look up from under the tree—the path keeps going, and it’s getting brighter.
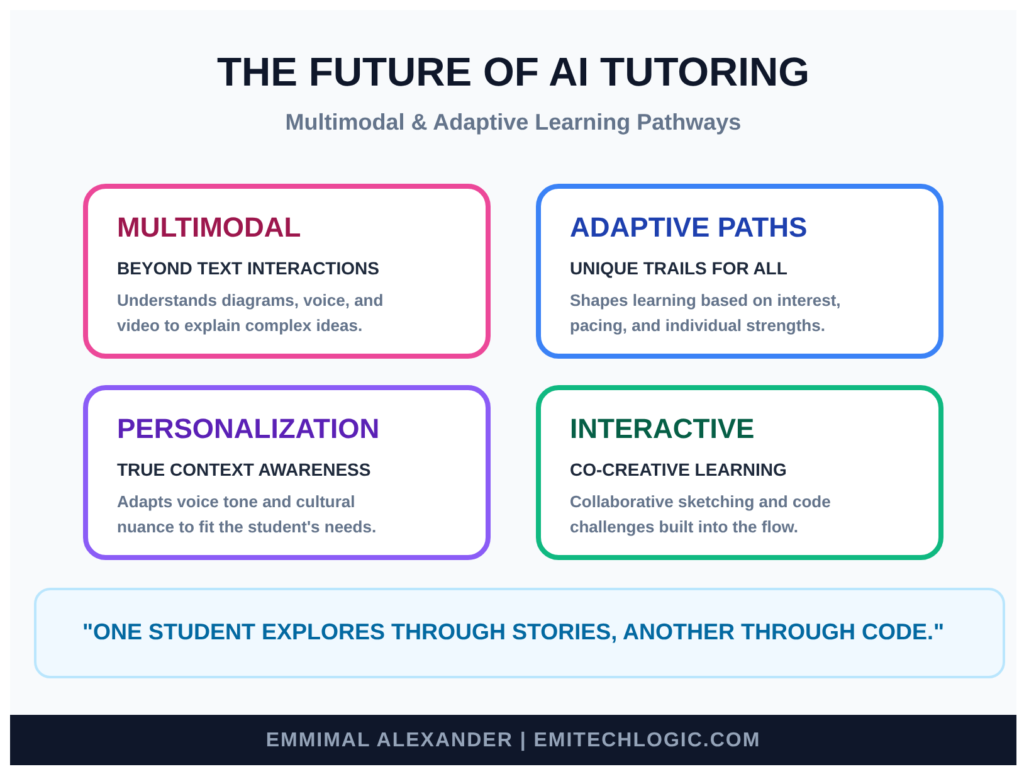
In the coming years, AI tutoring systems will grow in beautiful ways:
- Multimodal learning: Not just text. The tutor will look at diagrams, listen to your spoken questions, watch short videos with you, even draw sketches to explain ideas.
- Adaptive paths: It will quietly notice what excites you, where you learn fastest, and gently shape a unique trail—just for you. One student might explore through stories, another through code challenges, another through experiments.
- Deeper personalization: Combining voice tone, pacing, even cultural context to feel like a tutor who truly knows you.
Here’s a glimpse of what’s coming in multimodal and adaptive AI tutoring:
The heart of it will stay the same: accurate knowledge (thanks to RAG and vector databases), a kind voice, and a real desire to help someone learn.
For reference, here are common views of the RAG pipeline and modern AI tutor interfaces today:
We’ve walked far together—from the first spark of an idea to a working, thoughtful AI-powered tutor with RAG and vector databases in 2025.
Whatever you build next, carry this quiet care with you.
Conclusion: Empowering Learners with Technology
Recap of AI Tutor Building Journey
We started with a simple truth: every student deserves teaching that fits them perfectly.
Plain large language models are wonderful talkers, but they sometimes wander from facts. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) changes that by handing the model trusted knowledge before it speaks—turning a clever voice into a reliable teacher.
The key pieces we brought together:
- A fast, natural Large Language Model (via Groq) as the gentle voice.
- Vector databases (like Pinecone) as the smart librarian, using embeddings for semantic search.
- Clean chunks of educational material as the trusted knowledge base.
- A smooth RAG pipeline that retrieves exactly what’s needed.
- A welcoming Streamlit interface as the front door.
By the end, you have a working, accurate, personal AI-powered tutor—one that grounds every answer in real sources and speaks with patience and clarity.
This is the quiet power of RAG and vector databases in 2025: making advanced AI safe and useful for real teaching.
Call to Action: Start Building Your Custom AI Tutor
The complete, ready-to-run code for this tutorial is now available on GitHub!
GitHub Repository: Clone, fork, and start building your own AI tutor
Simply:
- Clone the repo:
git clone https://github.com/Emmimal/ai-powered-tutor-rag-vector-db.git - Install dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt - Add your API keys to
.env - Index your knowledge base:
python ingest.py - Launch the tutor:
streamlit run app.py
The code is all here—simple, clear, and ready to run.
Fork it, change the subject, add your own PDFs, try different embeddings or models. Make it teach math, history, coding, languages—whatever calls to you.
Start small: one textbook, ten test questions. Watch it answer accurately. Then grow it.
Every learner you help—maybe a student struggling alone, or a curious mind far from a classroom—will feel the difference.
The tools are free or low-cost. The path is open.
Build your own AI tutor today. Someone is waiting for exactly the teacher you’ll create.
Resources and Further Reading
- Full Source Code on GitHub: https://github.com/Emmimal/ai-powered-tutor-rag-vector-db/
- LangChain Documentation: https://python.langchain.com/docs/get_started/introduction
- Groq Quickstart: https://console.groq.com/docs/quickstart
- Pinecone Docs: https://docs.pinecone.io/docs/overview
- Hugging Face Embeddings: https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=sentence-similarity
- Ragas Evaluation: https://docs.ragas.io/
- Streamlit Tutorials: https://docs.streamlit.io/
- Key Paper: “Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks” (Lewis et al., 2020) – https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401
FAQs
1. How does RAG improve AI tutor accuracy compared to standard LLMs?
In 2025, standard Large Language Models (LLMs) often struggle with “hallucinations” or providing outdated information. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) solves this by grounding the AI tutor’s responses in specific, verified educational materials. Instead of relying on internal training data, the tutor retrieves the most relevant chunks from your textbook or curriculum database first, ensuring every answer is factual and context-aware.
2. Why are vector databases essential for building an AI-powered tutoring system?
Traditional relational databases (SQL) are designed for exact keyword matches, whereas vector databases use “semantic search” to understand the intent behind a student’s question. They store data as high-dimensional numerical representations (embeddings), allowing the tutor to find relevant teaching concepts even if the student uses different terminology than the source text. This ensures lightning-fast retrieval even as your library of learning materials scales to millions of pages.
3. Which is the best vector database for education apps: Pinecone, Weaviate, or Milvus?
The choice depends on your deployment needs:
Milvus: Preferred for massive, enterprise-scale AI tutors that need to handle billions of vectors with high performance.
Pinecone: Best for developers who want a fully managed, serverless experience with minimal infrastructure overhead.
Weaviate: Ideal for open-source flexibility and those requiring Hybrid Search (combining keyword and vector search) out of the box.
4. How can I reduce latency in a real-time RAG-based AI tutor?
To achieve sub-second response times for student interactions, developers in 2025 use several optimization strategies:
Caching: Implement caching for frequently asked student questions to bypass the full RAG pipeline.
Indexing Algorithms: Use HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World) for fast approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) searches.
Embedding Models: Select low-latency models like bge-small or all-MiniLM-L6-v2 for faster query vectorization.
5. Can an AI tutor built with RAG handle multi-modal data like images and video?
Yes. Multimodal RAG is a key trend. By using multimodal embedding models, you can convert educational diagrams, lecture videos, and text into a shared vector space. This allows your AI tutor to retrieve a specific timestamp in a video or a relevant chart from a textbook to help explain a concept visually to the student.
Test Your Knowledge: Interactive Quiz on RAG and AI Tutors
How well did you follow our journey under the tree? Take this quick, fun quiz to check your understanding of building an AI-powered tutor with RAG and vector databases. It’s designed to reinforce the key concepts—LLMs, Retrieval-Augmented Generation, vector databases, and more.
The quiz is fully interactive, shows instant feedback, calculates your score, and highlights correct answers. Perfect for solidifying your learning on RAG pipelines in 2025.
Ready? Start the Quiz Below!
Mastering RAG & Vector Databases
Test your knowledge on building AI-powered tutors.
Interactive Learning Module • RAG Architecture






Leave a Reply