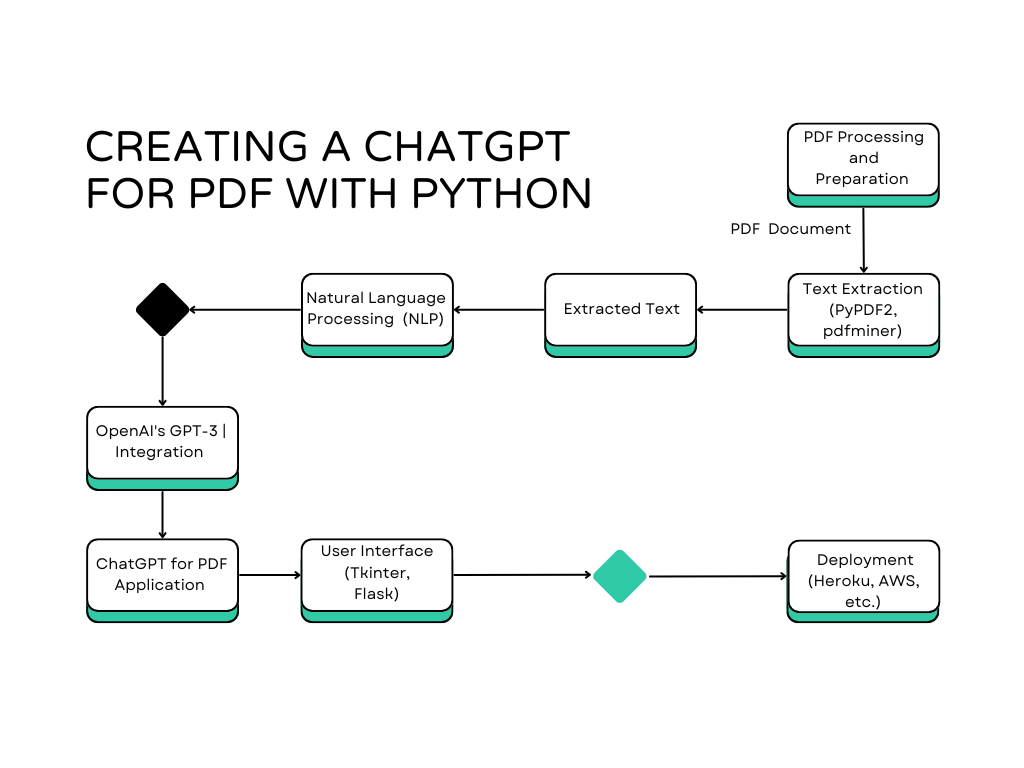
How to Create a Chatgpt for PDF with Python
We live in the world of automation and artificial intelligence; creating a chatbot that can read and interact with PDFs can be incredibly useful. Whether you need to summarize lengthy documents, answer specific questions, or extract valuable insights from PDFs, combining the power of Python with advanced natural language processing (NLP) capabilities can smoothen your workflow. This blog post will guide you through the process of building a ChatGPT for PDFs using Python. We will cover everything from PDF text extraction, setting up a conversational AI, to deploying the app with Flask, and ensuring a user-friendly interface with Tkinter.
Introduction to PDF Processing and NLP
PDFs are everywhere in the business world and hold a lot of information in a portable format. However, getting and processing data from PDFs can be difficult. By using Python’s powerful libraries and OpenAI’s GPT, we can create an interactive PDF chat application. This tool will enable users to ask questions and receive detailed responses based on the content of PDF documents.
Setting Up Your Python Environment – Chatgpt for PDF
Before we start coding, we need to set up our Python environment with the necessary libraries. Open your terminal and create a new project directory:
mkdir ChatPDFApp
cd ChatPDFApp
Installing Required Libraries
Create a requirements.txt file to list the libraries we need:
langchain
openai
pdfminer.six
tkinter
Then, install these libraries using pip:
pip install -r requirements.txt
Project Structure
Here’s the structure of our project:
ChatPDFApp/
│
├── app.py # Main application script
├── pdf_utils.py # PDF processing utilities
├── chat_utils.py # ChatGPT interaction utilities
├── ui.py # Tkinter user interface
├── requirements.txt # List of required Python libraries
└── README.md # Project description and instructions
Extracting Text from PDFs
To handle PDF text extraction, we will use pdfminer.six, a Python PDF library. Create a file named pdf_utils.py and add the following code:
import io
from pdfminer.high_level import extract_text
from pdfminer.pdfparser import PDFSyntaxError
def extract_text_from_pdf(pdf_path):
try:
text = extract_text(pdf_path)
if not text.strip():
raise ValueError("The PDF appears to be empty or contains non-text content.")
return text
except FileNotFoundError:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"The file at {pdf_path} was not found.")
except PDFSyntaxError:
raise PDFSyntaxError("Error reading the PDF file. It may be corrupted or not a valid PDF.")
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"An unexpected error occurred: {str(e)}")
Let’s break down the provided text and code step by step:
Extracting Text from PDFs
This section explains how to extract text from PDF files using a Python library called pdfminer.six.
Library and File Setup
- pdfminer.six: This is a best Python library designed for extracting text from PDF documents. It’s well-suited for handling complex PDF files.
- Create a file: You need to create a new Python file named
pdf_utils.py. This file will contain the code for extracting text from PDFs.
Code Explanation
import io
from pdfminer.high_level import extract_text
from pdfminer.pdfparser import PDFSyntaxError
Imports
The code imports necessary modules from the pdfminer.six library. extract_text is a function used to extract text from PDF files, and PDFSyntaxError is an exception that handles syntax errors in PDFs.
def extract_text_from_pdf(pdf_path):
try:
text = extract_text(pdf_path)
if not text.strip():
raise ValueError("The PDF appears to be empty or contains non-text content.")
return text
except FileNotFoundError:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"The file at {pdf_path} was not found.")
except PDFSyntaxError:
raise PDFSyntaxError("Error reading the PDF file. It may be corrupted or not a valid PDF.")
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"An unexpected error occurred: {str(e)}")
Function Definition
The function extract_text_from_pdf is defined to take a single argument pdf_path, which is the path to the PDF file.
Try Block: The try block attempts to extract text from the PDF file.
extract_text(pdf_path): This function call extracts the text content from the PDF file located atpdf_path.- Check for Empty Text: If the extracted text is empty or contains only non-text content, a
ValueErroris raised with an appropriate message. - Return Text: If everything goes well, the extracted text is returned.
Except Blocks
These blocks handle various potential errors:
- FileNotFoundError: This is raised if the file specified by
pdf_pathis not found. - PDFSyntaxError: This handles cases where the PDF file cannot be read due to corruption or invalid format.
- Generic Exception: Any other unexpected errors are caught here, and an appropriate error message is raised.
This setup allows you to create a utility for extracting text from PDF files in a reliable and error-handling manner, which is essential for building more complex applications like a chatbot that can interact with PDF content.
Integrating NLP with OpenAI’s GPT
Next, we need to integrate our PDF text extraction with OpenAI’s GPT. Create a file named chat_utils.py:
from langchain import OpenAI, ConversationChain
def initialize_conversation(api_key):
llm = OpenAI(api_key=api_key)
conversation = ConversationChain(llm=llm)
return conversation
def chat_with_pdf(conversation, pdf_text, user_query):
prompt = (f"You are an AI assistant. Below is the content of a PDF document:\n\n"
f"{pdf_text}\n\n"
f"User query: {user_query}\n\n"
f"Please provide a detailed response based on the document content.")
try:
response = conversation.generate(prompt)
return response
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"An error occurred while generating the response: {str(e)}")
let’s break down the provided text and code for integrating Natural Language Processing (NLP) with OpenAI’s GPT to interact with the text extracted from PDFs.
Integrating NLP with OpenAI’s GPT
Purpose: This section explains how to integrate the text extracted from PDF files with OpenAI’s GPT model to create an interactive chat experience.
Library and File Setup
Create a file: You need to create a new Python file named chat_utils.py. This file will contain the code for initializing the conversation with GPT and handling user queries based on PDF content.
Code Explanation
from langchain import OpenAI, ConversationChain
- Imports: The code imports necessary classes from the
langchainlibrary.OpenAIis used to interact with OpenAI’s GPT, andConversationChainmanages the conversation flow.
def initialize_conversation(api_key):
llm = OpenAI(api_key=api_key)
conversation = ConversationChain(llm=llm)
return conversation
Function Definition: initialize_conversation:
- Parameters: Takes
api_keyas an argument, which is your API key for accessing OpenAI’s GPT. - OpenAI Initialization:
OpenAI(api_key=api_key)initializes the connection to OpenAI using the provided API key. - Conversation Chain:
ConversationChain(llm=llm)creates a conversation chain using the initialized OpenAI model. - Return: The function returns the
conversationobject.
def chat_with_pdf(conversation, pdf_text, user_query):
prompt = (f"You are an AI assistant. Below is the content of a PDF document:\n\n"
f"{pdf_text}\n\n"
f"User query: {user_query}\n\n"
f"Please provide a detailed response based on the document content.")
try:
response = conversation.generate(prompt)
return response
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"An error occurred while generating the response: {str(e)}")
Function Definition: chat_with_pdf:
- Parameters: Takes three arguments:
conversation: The conversation object initialized byinitialize_conversation.pdf_text: The text extracted from the PDF document.user_query: The user’s query or question based on the PDF content.
- Prompt Construction: Constructs a prompt string for GPT. The prompt includes:
- A brief instruction to GPT (“You are an AI assistant”).
- The content of the PDF document.
- The user’s query.
- Generate Response:
conversation.generate(prompt)uses the conversation object to generate a response based on the prompt. - Return: Returns the response generated by GPT.
- Exception Handling: If an error occurs during response generation, it raises an exception with an appropriate error message.
This setup enables you to create a conversational interface that can intelligently respond to user queries based on the content of PDF documents. The integration of PDF text extraction and GPT provides a powerful tool for automated document analysis and interaction.

Building a User Interface with Tkinter
For a user-friendly interface, we’ll use Tkinter. Create a file named ui.py:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog, scrolledtext, messagebox
from pdf_utils import extract_text_from_pdf
from chat_utils import initialize_conversation, chat_with_pdf
class ChatPDFApp:
def __init__(self, root, api_key):
self.root = root
self.root.title("ChatPDF Application")
self.api_key = api_key
self.conversation = initialize_conversation(api_key)
self.pdf_text = ""
self.setup_ui()
def setup_ui(self):
self.select_pdf_button = tk.Button(self.root, text="Select PDF", command=self.load_pdf)
self.select_pdf_button.pack(pady=10)
self.query_label = tk.Label(self.root, text="Enter your query:")
self.query_label.pack(pady=5)
self.query_entry = tk.Entry(self.root, width=50)
self.query_entry.pack(pady=5)
self.ask_button = tk.Button(self.root, text="Ask", command=self.ask_question)
self.ask_button.pack(pady=10)
self.response_text = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(self.root, wrap=tk.WORD, width=80, height=20)
self.response_text.pack(pady=10)
def load_pdf(self):
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(filetypes=[("PDF files", "*.pdf")])
if file_path:
try:
self.pdf_text = extract_text_from_pdf(file_path)
messagebox.showinfo("Success", "PDF loaded successfully!")
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("Error", str(e))
def ask_question(self):
user_query = self.query_entry.get()
if not user_query:
messagebox.showwarning("Warning", "Please enter a query.")
return
if not self.pdf_text:
messagebox.showwarning("Warning", "Please load a PDF first.")
return
try:
response = chat_with_pdf(self.conversation, self.pdf_text, user_query)
self.response_text.insert(tk.END, f"Q: {user_query}\nA: {response}\n\n")
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("Error", str(e))
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
api_key = "your_openai_api_key" # Replace with your actual OpenAI API key
app = ChatPDFApp(root, api_key)
root.mainloop()
let’s break down the provided text and code for building a user-friendly interface using Tkinter to interact with PDFs and OpenAI’s GPT.
Building a User Interface with Tkinter
- Purpose: This section explains how to create a graphical user interface (GUI) using Tkinter, which allows users to interact with a PDF file and ask questions based on its content.
Library and File Setup
- Create a file: You need to create a new Python file named
ui.py. This file will contain the code for the GUI.
Code Explanation
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog, scrolledtext, messagebox
from pdf_utils import extract_text_from_pdf
from chat_utils import initialize_conversation, chat_with_pdf
- Imports: The code imports necessary modules from Tkinter for creating the GUI (
tk,filedialog,scrolledtext,messagebox). It also imports functions from the previously createdpdf_utilsandchat_utilsfiles.
class ChatPDFApp:
def __init__(self, root, api_key):
self.root = root
self.root.title("ChatPDF Application")
self.api_key = api_key
self.conversation = initialize_conversation(api_key)
self.pdf_text = ""
self.setup_ui()
Class Definition: ChatPDFApp:
- Constructor (
__init__): Initializes the main application window. - Parameters:
root: The main Tkinter window.api_key: The API key for OpenAI.
- Window Title: Sets the window title to “ChatPDF Application”.
- Conversation Initialization: Initializes the conversation with GPT using the provided API key.
- PDF Text: Initializes an empty string to hold the PDF text content.
- UI Setup: Calls the
setup_uimethod to create the user interface components.
def setup_ui(self):
self.select_pdf_button = tk.Button(self.root, text="Select PDF", command=self.load_pdf)
self.select_pdf_button.pack(pady=10)
self.query_label = tk.Label(self.root, text="Enter your query:")
self.query_label.pack(pady=5)
self.query_entry = tk.Entry(self.root, width=50)
self.query_entry.pack(pady=5)
self.ask_button = tk.Button(self.root, text="Ask", command=self.ask_question)
self.ask_button.pack(pady=10)
self.response_text = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(self.root, wrap=tk.WORD, width=80, height=20)
self.response_text.pack(pady=10)
Method: setup_ui:
- PDF Selection Button: A button for selecting PDF files, which triggers the
load_pdfmethod. - Query Label: A label instructing the user to enter their query.
- Query Entry: A text entry box for the user to type their query.
- Ask Button: A button to submit the query, which triggers the
ask_questionmethod. - Response Text Box: A scrollable text box to display responses from GPT.
def load_pdf(self):
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(filetypes=[("PDF files", "*.pdf")])
if file_path:
try:
self.pdf_text = extract_text_from_pdf(file_path)
messagebox.showinfo("Success", "PDF loaded successfully!")
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("Error", str(e))
Method: load_pdf
- File Dialog: Opens a file dialog to select a PDF file.
- File Path: Checks if a file was selected.
- Extract Text: Uses
extract_text_from_pdfto extract text from the selected PDF. - Success Message: Shows a success message if the PDF is loaded successfully.
- Error Handling: Shows an error message if there’s an issue loading the PDF.
def ask_question(self):
user_query = self.query_entry.get()
if not user_query:
messagebox.showwarning("Warning", "Please enter a query.")
return
if not self.pdf_text:
messagebox.showwarning("Warning", "Please load a PDF first.")
return
try:
response = chat_with_pdf(self.conversation, self.pdf_text, user_query)
self.response_text.insert(tk.END, f"Q: {user_query}\nA: {response}\n\n")
except Exception as e:
messagebox.showerror("Error", str(e))
Method: ask_question
- Get User Query: Retrieves the user’s query from the entry box.
- Empty Query Warning: Shows a warning if no query is entered.
- PDF Not Loaded Warning: Shows a warning if no PDF is loaded.
- Generate Response: Uses
chat_with_pdfto generate a response based on the PDF content and user query. - Display Response: Inserts the query and response into the scrollable text box.
- Error Handling: Shows an error message if there’s an issue generating the response.
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = tk.Tk()
api_key = "your_openai_api_key" # Replace with your actual OpenAI API key
app = ChatPDFApp(root, api_key)
root.mainloop()
Main Block
- Root Window: Creates the main Tkinter window.
- API Key: Replace
"your_openai_api_key"with your actual OpenAI API key. - App Instance: Creates an instance of
ChatPDFAppwith the root window and API key. - Main Loop: Starts the Tkinter main loop to run the application.
This setup provides a complete GUI for loading PDF files, entering user queries, and displaying responses generated by OpenAI’s GPT, making it a user-friendly application for interacting with PDF documents.
Deploying Your Chatgpt Application with Flask
For broader accessibility, we can deploy our application as a web app using Flask. First, install Flask:
pip install Flask
Create app.py for the Flask application:
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify, render_template
from pdf_utils import extract_text_from_pdf
from chat_utils import initialize_conversation, chat_with_pdf
app = Flask(__name__)
api_key = "your_openai_api_key"
conversation = initialize_conversation(api_key)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/upload', methods=['POST'])
def upload_pdf():
file = request.files['file']
if file:
try:
pdf_text = extract_text_from_pdf(file)
return jsonify({'pdf_text': pdf_text}), 200
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': str(e)}), 400
return jsonify({'error': 'No file provided'}), 400
@app.route('/ask', methods=['POST'])
def ask_question():
data = request.json
pdf_text = data.get('pdf_text', '')
user_query = data.get('user_query', '')
if not pdf_text or not user_query:
return jsonify({'error': 'PDF text and user query are required'}), 400
try:
response = chat_with_pdf(conversation, pdf_text, user_query)
return jsonify({'response': response}), 200
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': str(e)}), 500
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
let’s break down the provided code for creating a Flask application that allows users to upload PDF files and interact with their content using OpenAI’s GPT
Code Explanation
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify, render_template
from pdf_utils import extract_text_from_pdf
from chat_utils import initialize_conversation, chat_with_pdf
Imports
Flask,request,jsonify,render_templateare imported from theflasklibrary to handle web requests and responses.- Functions
extract_text_from_pdf,initialize_conversation, andchat_with_pdfare imported from the previously created utility files.
app = Flask(__name__)
api_key = "your_openai_api_key"
conversation = initialize_conversation(api_key)
Flask App Initialization
- The code initializes a Flask application.
- The OpenAI API key is set (replace
"your_openai_api_key"with your actual API key). - A conversation object is initialized using the OpenAI API key
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html')
Route Definition: /
- This route handles GET requests to the root URL.
- It renders an
index.htmltemplate (assumed to be a simple HTML file for the web interface).
@app.route('/upload', methods=['POST'])
def upload_pdf():
file = request.files['file']
if file:
try:
pdf_text = extract_text_from_pdf(file)
return jsonify({'pdf_text': pdf_text}), 200
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': str(e)}), 400
return jsonify({'error': 'No file provided'}), 400
Route Definition: /upload
This route handles POST requests for uploading PDF files.request.files['file'] retrieves the uploaded file from the request.
File Processing:
- If a file is provided, it tries to extract text from the PDF using
extract_text_from_pdf. - Success: Returns the extracted PDF text as a JSON response with a 200 status code.
- Error: Returns an error message as a JSON response with a 400 status code.
No File Provided: Returns an error message as a JSON response with a 400 status code.
@app.route('/ask', methods=['POST'])
def ask_question():
data = request.json
pdf_text = data.get('pdf_text', '')
user_query = data.get('user_query', '')
if not pdf_text or not user_query:
return jsonify({'error': 'PDF text and user query are required'}), 400
try:
response = chat_with_pdf(conversation, pdf_text, user_query)
return jsonify({'response': response}), 200
except Exception as e:
return jsonify({'error': str(e)}), 500
Route Definition: /ask
This route handles POST requests for asking questions based on the PDF content.
Retrieve Data:
request.jsonretrieves the JSON data sent in the request.- Extracts
pdf_textanduser_queryfrom the JSON data.
Validation:
- If either
pdf_textoruser_queryis missing, returns an error message with a 400 status code.
Generate Response:
- Uses
chat_with_pdfto generate a response based on the provided PDF text and user query. - Success: Returns the generated response as a JSON response with a 200 status code.
- Error: Returns an error message as a JSON response with a 500 status code.
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(debug=True)
Main Block
- Runs the Flask application in debug mode, allowing for easier debugging and development.
This setup provides a web-based application where users can upload PDF files, extract text from them, and ask questions based on the content, receiving responses generated by OpenAI’s GPT model.
HTML Template
Create a templates folder and add index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>ChatPDF App</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>ChatPDF Application</h1>
<form id="pdfForm" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="file" id="fileInput" accept=".pdf">
<button type="button" onclick="uploadPDF()">Upload PDF</button>
</form>
<div id="pdfTextContainer" style="display:none;">
<h2>PDF Text</h2>
<pre id="pdfText"></pre>
<h2>Ask a Question</h2>
<input type="text" id="queryInput">
<button type="button" onclick="askQuestion()">Ask</button>
<div id="responseContainer">
<h3>Response</h3>
<p id="responseText"></p>
</div>
</div>
<script>
async function uploadPDF() {
const fileInput = document.getElementById('fileInput');
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append('file', fileInput.files[0]);
const response = await fetch('/upload', {
method: 'POST',
body: formData
});
const data = await response.json();
if (response.ok) {
document.getElementById('pdfText').textContent = data.pdf_text;
document.getElementById('pdfTextContainer').style.display = 'block';
} else {
alert(data.error);
}
}
async function askQuestion() {
const pdfText = document.getElementById('pdfText').textContent;
const userQuery = document.getElementById('queryInput').value;
const response = await fetch('/ask', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({ pdf_text: pdfText, user_query: userQuery })
});
const data = await response.json();
if (response.ok) {
document.getElementById('responseText').textContent = data.response;
} else {
alert(data.error);
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Enhancing the ChatGPT for PDFs
Adding OCR Capabilities
For scanned PDFs, you might need Optical Character Recognition (OCR). Using pytesseract, we can add OCR capabilities. Install pytesseract and Pillow:
pip install pytesseract Pillow
Update pdf_utils.py:
import io
from pdfminer.high_level import extract_text
from pdfminer.pdfparser import PDFSyntaxError
from PIL import Image
import pytesseract
def extract_text_from_pdf(pdf_path):
try:
text = extract_text(pdf_path)
if not text.strip():
raise ValueError("The PDF appears to be empty or contains non-text content.")
return text
except FileNotFoundError:
raise FileNotFoundError(f"The file at {pdf_path} was not found.")
except PDFSyntaxError:
raise PDFSyntaxError("Error reading the PDF file. It may be corrupted or not a valid PDF.")
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"An unexpected error occurred: {str(e)}")
def ocr_pdf_images(pdf_path):
try:
images = convert_from_path(pdf_path)
text = ""
for image in images:
text += pytesseract.image_to_string(image)
return text
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"An error occurred during OCR processing: {str(e)}")
Conclusion – Chatgpt
In this blog post, we’ve built a comprehensive ChatGPT application for PDFs using Python. We’ve covered how to extract text from PDFs, integrate NLP using OpenAI’s GPT, create a user-friendly interface with Tkinter, and deploy the app using Flask. Additionally, we enhanced the application with OCR capabilities for handling scanned PDFs.
By following these steps, you can develop a powerful tool for interacting with PDF documents, making it easier to extract and process valuable information. This application demonstrates the flexibility and capability of Python when combined with modern AI technologies.
External Resources
- PyPDF2 Documentation
- pdfminer.six Documentation
- LangChain Documentation
- Flask Documentation
- Python Official Documentation






Leave a Reply