How to Develop a PDF-to-Audio Converter with Python
Introduction – PDF-to-Audio Converter
Have you ever found yourself wanting to listen to the content of a PDF instead of reading it? Whether you’re busy, multitasking, or simply prefer audio formats, Well, you’re in luck! In this blog post, we will guide you through creating a PDF-to-Audio converter using Python. This tool will take a PDF file, extract its text, convert the text into audio, and save it as an MP3 file.
We’ll be using some powerful Python libraries to accomplish this task: PyMuPDF for reading PDF files, Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) for converting text to speech, and Flask for creating a simple web interface. Let’s start! Before we begin coding, let’s observe how our PDF-to-Audio Converter Application works
Prerequisites
Before we start coding, make sure you have Python installed on your computer. You can download Python from python.org. We will also need to install a few Python libraries. Open your terminal and run the following commands:
pip install Flask
pip install PyMuPDF
pip install gTTS
These commands will install Flask, PyMuPDF, and Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS).
Setting Up the Project of PDF-to-Audio Converter
First, let’s create a project directory. Open your terminal and run:
mkdir pdf_to_audio
cd pdf_to_audio
Inside this directory, we will create the necessary files for our project:
app.py: This will contain our Flask application.templates/index.html: This will be our HTML file for the web interface.static/style.css: This will contain our CSS styles.
Let’s start by creating these files.
Creating the Flask Application for PDF-to-Audio Converter
app.py
Open your text editor or IDE and create a new file named app.py. This file will contain our Flask application.
First, let’s import the necessary modules and set up our Flask app:
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, send_file, jsonify
import os
import fitz # PyMuPDF
from gtts import gTTS # Google Text-to-Speech
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import threading
app = Flask(__name__)
app.secret_key = (Your Secret Key) # Replace with your own secret key
Flask Import and Setup
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, send_file, jsonify: This line imports necessary modules from Flask, which is a Python web framework. These modules help manage web requests, display templates, send files, and convert Python data into JSON format for responses.
Operating System (os) Import
import os: This module provides functions for interacting with the operating system. We used here to perform operations related to files and directories.
PyMuPDF (fitz) Import
import fitz: This is a Python library (PyMuPDF) used for reading PDF files and extracting text from them.
Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) Import
from gtts import gTTS: This library allows us to convert text into spoken audio (MP3 files) using Google’s Text-to-Speech API.
ThreadPoolExecutor and Threading Import
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor: This module provides a high-level interface for asynchronously executing functions using threads or processes.import threading: Threading is Python’s way of achieving concurrency, allowing multiple tasks to run concurrently.
Flask App Setup
app = Flask(__name__): Creates a new Flask application instance.app.secret_key = (Your Secret Key): Replace this with your own secret key. This line sets a secret key for the Flask application. The secret key is used to secure session data and other cryptographic operations within Flask. It should be kept private and secure.
So far,
- We’re setting up a web application using Flask.
- We import modules that help us handle web requests, work with PDFs, convert text to speech, and manage concurrent tasks.
- The secret key ensures that session data remains secure and encrypted within our web application.
Status Tracking for PDF-to-Audio converter
We will keep track of the conversion status using a shared dictionary. We’ll use a lock to ensure thread-safe updates to this dictionary:
status = {
"current_chunk": 0,
"total_chunks": 0,
"status": "idle"
}
status_lock = threading.Lock()
def update_status(current, total, state):
with status_lock:
status["current_chunk"] = current
status["total_chunks"] = total
status["status"] = state
Shared Status Dictionary
status = { "current_chunk": 0, "total_chunks": 0, "status": "idle" }- Here,
statusis a dictionary that stores information about the current state of a conversion process. current_chunk: Tracks the number of the current chunk (part) of the PDF being processed.total_chunks: Indicates the total number of chunks (parts) in the PDF that need to be processed.status: Describes the current status of the conversion process, which starts as “idle”.
Thread Lock for Synchronization
status_lock = threading.Lock(): This line creates aLockobject namedstatus_lock.- A
Lockin Python ensures that only one thread can access a shared resource (in this case, thestatusdictionary) at a time. - This prevents conflicts and ensures that updates to the
statusdictionary are handled safely when multiple threads are involved.
Update Status Function
def update_status(current, total, state):
- This function
update_statustakes three parameters:current: The current chunk number being processed.total: The total number of chunks in the PDF.state: The current state of the conversion process (e.g., “processing”, “completed”, “error”).
with status_lock
- Using
with status_lock:ensures that the code block inside it is executed while holding thestatus_lock. This prevents other threads from modifyingstatusconcurrently.
Inside the with block
status["current_chunk"] = current: Updates thecurrent_chunkin thestatusdictionary with the providedcurrentvalue.status["total_chunks"] = total: Updates thetotal_chunksin thestatusdictionary with the providedtotalvalue.status["status"] = state: Updates thestatusin thestatusdictionary with the providedstatevalue, indicating the current state of the conversion process.
In simpler terms:
- We use a dictionary named
statusto keep track of where we are in converting a PDF to audio. - The
status_lockensures that only one part of the program can update this dictionary at a time, preventing mix-ups. - The
update_statusfunction makes it easy to tell what part of the PDF we’re on and if the conversion is done or still going.
PDF to Text Conversion – PDF-to-Audio Converter
Next, we need a function to convert the PDF to text. We will use PyMuPDF for this:
def pdf_to_text(pdf_file):
text = ""
try:
doc = fitz.open(pdf_file)
for page_num in range(len(doc)):
page = doc.load_page(page_num)
text += page.get_text()
doc.close()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error reading PDF: {e}")
return None
return text
Function Definition
def pdf_to_text(pdf_file):
- This line defines a function named
pdf_to_textthat takespdf_fileas a parameter. This parameter is expected to be the path to a PDF file.
Initialization of text Variable
text = ""
textis initialized as an empty string. This variable will accumulate all the text content extracted from the PDF.
Opening and Reading the PDF File – PDF-to-Audio Converter
try:
doc = fitz.open(pdf_file)
for page_num in range(len(doc)):
page = doc.load_page(page_num)
text += page.get_text()
doc.close()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error reading PDF: {e}")
return None
fitz.open(pdf_file): Opens the PDF file specified by pdf_file using PyMuPDF (also known as fitz).
for page_num in range(len(doc)): Iterates through each page in the PDF.
page = doc.load_page(page_num): Loads the current page from the PDF.text += page.get_text(): Retrieves the text content of the current page and appends it to thetextvariable.
doc.close(): Closes the PDF document after all pages have been processed.
except Exception as e: Handles any exceptions that may occur during the PDF reading process.
- If an error occurs (
Exception), it prints an error message indicating the issue (f"Error reading PDF: {e}"). - It then returns
Noneto indicate that the function did not successfully extract text from the PDF.
In summarry,
- The
pdf_to_textfunction reads a PDF file (pdf_file) and extracts its text content. - It uses PyMuPDF (
fitz) to open the PDF and iterate through each page to get the text. - If there’s an error during the reading process, it prints an error message and returns
None. - Otherwise, it returns all the text extracted from the PDF as a single string.
Returning Extracted Text
return text
- If the PDF is read successfully without any exceptions, the function returns the accumulated
textextracted from all pages of the PDF.
Text to MP3 Conversion
We also need a function to convert text to MP3. We will use Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) for this:
def text_to_mp3_chunk(chunk, chunk_index, output_directory):
try:
tts = gTTS(text=chunk, lang='en')
temp_chunk_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f'chunk_{chunk_index}.mp3')
tts.save(temp_chunk_path)
print(f"Saved chunk {chunk_index} to {temp_chunk_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error converting chunk {chunk_index} to MP3: {e}")
Here’s a simplified explanation of the Python function text_to_mp3_chunk that uses Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS) to convert a chunk of text into an MP3 file:
Function Definition
def text_to_mp3_chunk(chunk, chunk_index, output_directory):
This line defines a function named text_to_mp3_chunk that takes three parameters:
chunk: The text content to be converted into speech.chunk_index: The index or identifier of the current chunk.output_directory: The directory where the MP3 file will be saved.
Text-to-Speech Conversion – PDF-to-Audio Converter
try:
tts = gTTS(text=chunk, lang='en')
temp_chunk_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f'chunk_{chunk_index}.mp3')
tts.save(temp_chunk_path)
print(f"Saved chunk {chunk_index} to {temp_chunk_path}")
gTTS(text=chunk, lang='en'): Creates a gTTS (Google Text-to-Speech) object with the specifiedchunkof text and language (‘en’ for English).temp_chunk_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f'chunk_{chunk_index}.mp3'): Constructs the path where the MP3 file will be saved. The file name includeschunk_indexto differentiate between different chunks.tts.save(temp_chunk_path): Saves the synthesized speech as an MP3 file attemp_chunk_path.print(f"Saved chunk {chunk_index} to {temp_chunk_path}"):- Prints a message confirming the successful saving of the MP3 file.
Error Handling
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error converting chunk {chunk_index} to MP3: {e}")
- If an error occurs during the text-to-speech conversion process (
Exception), it prints an error message indicating the issue (f"Error converting chunk {chunk_index} to MP3: {e}").
In simpler terms:
- The
text_to_mp3_chunkfunction converts a piece of text (chunk) into spoken audio using Google Text-to-Speech. - It saves the synthesized speech as an MP3 file in the specified
output_directory. - If successful, it prints a confirmation message with the file path.
- If there’s an error during the conversion process, it prints an error message describing the issue
Combining MP3 Chunks
To handle large texts, we will split the text into chunks, convert each chunk to MP3, and then combine these chunks into a single MP3 file:
def combine_mp3_chunks(chunk_count, output_directory, final_mp3_path):
try:
with open(final_mp3_path, 'wb') as final_mp3_file:
for i in range(chunk_count):
chunk_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f'chunk_{i}.mp3')
with open(chunk_path, 'rb') as chunk_file:
final_mp3_file.write(chunk_file.read())
os.remove(chunk_path) # Clean up chunk file
print(f"MP3 saved to {final_mp3_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error combining MP3 chunks: {e}")
Function Definition
def combine_mp3_chunks(chunk_count, output_directory, final_mp3_path):
This line defines a function named combine_mp3_chunks that takes three parameters:
chunk_count: The total number of MP3 chunks to combine.output_directory: The directory where the MP3 chunks are stored.final_mp3_path: The path where the final combined MP3 file will be saved.
Combining MP3 Chunks
try:
with open(final_mp3_path, 'wb') as final_mp3_file:
for i in range(chunk_count):
chunk_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f'chunk_{i}.mp3')
with open(chunk_path, 'rb') as chunk_file:
final_mp3_file.write(chunk_file.read())
os.remove(chunk_path) # Clean up chunk file
print(f"MP3 saved to {final_mp3_path}")
with open(final_mp3_path, 'wb') as final_mp3_file:: Opensfinal_mp3_pathin write mode ('wb'), creating a new file for the final combined MP3.for i in range(chunk_count):: Iterates through each chunk index from 0 tochunk_count - 1.
chunk_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f'chunk_{i}.mp3'): Constructs the path to each MP3 chunk file.with open(chunk_path, 'rb') as chunk_file:: Openschunk_pathin read mode ('rb') to read its content.final_mp3_file.write(chunk_file.read()): Writes the content of the current chunk file (chunk_file) to the final MP3 file (final_mp3_file).
os.remove(chunk_path): Deletes (removes) the current chunk file (chunk_path) after its content has been written to the final MP3 file to clean up disk space.
Error Handling
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error combining MP3 chunks: {e}")
- If an error occurs during the combination process (
Exception), it prints an error message describing the issue (f"Error combining MP3 chunks: {e}").
Let’s summarize this
- The
combine_mp3_chunksfunction takes multiple MP3 chunks stored inoutput_directory, combines them into a single MP3 file (final_mp3_path), and deletes the individual chunk files afterward. - It opens each chunk file, reads its content, writes it to the final MP3 file, and then removes the chunk file.
- If there’s an error during the process, it prints an error message explaining what went wrong.
Flask Routes
Now, let’s set up the routes for our Flask application:
- The home route (
/) will display the form to upload the PDF file. - The
/statusroute will return the current status of the conversion. - The
/download/<filename>route will handle the download of the MP3 file.
@app.route('/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def index():
if request.method == 'POST':
pdf_file = request.files['pdf_file']
if pdf_file.filename == '':
return "No file chosen"
mp3_output_directory = './uploads'
if not os.path.exists(mp3_output_directory):
os.makedirs(mp3_output_directory)
if pdf_file and pdf_file.filename.endswith('.pdf'):
try:
# Save the uploaded PDF file
pdf_path = os.path.join(mp3_output_directory, pdf_file.filename)
pdf_file.save(pdf_path)
print(f"PDF saved to {pdf_path}")
# Convert PDF to text
text = pdf_to_text(pdf_path)
if text:
print(f"Extracted text: {text[:500]}...") # Print first 500 characters for verification
# Convert text to MP3
mp3_filename = f"{os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(pdf_path))[0]}.mp3"
mp3_path = os.path.join(mp3_output_directory, mp3_filename)
print(f"Converting text to MP3 and saving to {mp3_path}...")
# Splitting the text into chunks
text_chunks = [text[i:i + 1000] for i in range(0, len(text), 1000)]
update_status(0, len(text_chunks), 'processing')
# Process chunks in parallel using ThreadPoolExecutor
with ThreadPoolExecutor() as executor:
futures = [executor.submit(text_to_mp3_chunk, chunk, i, mp3_output_directory) for i, chunk in enumerate(text_chunks)]
for i, future in enumerate(futures):
future.result() # Ensure each thread completes
update_status(i + 1, len(text_chunks), 'processing')
# Combine all chunks into a single MP3 file
combine_mp3_chunks(len(text_chunks), mp3_output_directory, mp3_path)
update_status(len(text_chunks), len(text_chunks), 'done')
return jsonify({"status": "done", "download_url": f"/download/{mp3_filename}"})
else:
print("Error converting PDF to text.")
return "Error converting PDF to text. Please try again."
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing PDF: {e}")
return "Error processing PDF. Please try again."
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/status', methods=['GET'])
def get_status():
with status_lock:
return jsonify(status)
@app.route('/download/<filename>')
def download(filename):
mp3_file_path = os.path.join('./uploads', filename)
try:
print(f"Attempting to send file: {mp3_file_path}")
return send_file(mp3_file_path, as_attachment=True)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error sending file: {e}")
return "Error sending file. Please try again."
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
Index Route (/)
This route handles both GET and POST requests.On POST request:
- It checks if a PDF file is uploaded (
pdf_file). - Saves the PDF file to
./uploadsdirectory. - Converts the PDF to text using
pdf_to_text. - Splits the text into chunks and converts each chunk to MP3 using
text_to_mp3_chunk. - Combines all MP3 chunks into a single MP3 file using
combine_mp3_chunks. - Updates conversion status using
update_status. - Returns JSON response with conversion status and download URL for the MP3.
On GET request or if no file is uploaded, it renders an index.html template for file upload.
Status Route (/status)
@app.route('/status', methods=['GET'])
def get_status():
with status_lock:
return jsonify(status)
- This route handles
GETrequests to/status. - It uses
status_lockto ensure thread-safe access tostatusdictionary. - Returns JSON response containing the current conversion status (
statusdictionary).
Download Route (/download/<filename>)
@app.route('/download/<filename>')
def download(filename):
mp3_file_path = os.path.join('./uploads', filename)
try:
print(f"Attempting to send file: {mp3_file_path}")
return send_file(mp3_file_path, as_attachment=True)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error sending file: {e}")
return "Error sending file. Please try again."
- This route handles requests to download the MP3 file identified by
<filename>. - Constructs the file path (
mp3_file_path) usingfilenamefrom./uploadsdirectory. - Attempts to send the file (
mp3_file_path) as an attachment for download usingsend_file. - Handles exceptions and prints errors if file sending fails.
Main Execution (__name__ == '__main__') and Debug Mode
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
- This block ensures that the Flask application (
app) runs when this script is executed directly. debug=Trueenables debug mode in Flask, providing detailed error messages and auto-reloading the server when code changes.
In simpler terms:
- The Flask application provides routes (
/,/status,/download/<filename>) for uploading a PDF, checking conversion status, and downloading the converted MP3. - It handles file uploads, converts PDF to text, splits text into manageable chunks, converts each chunk to MP3, combines MP3 chunks into a single file, and updates status accordingly.
- Error handling ensures that any issues during these processes are logged, and appropriate messages are returned to users.
Creating the HTML Template for PDF-to-Audio Converter
Next, we need to create the HTML template for our web interface.
templates/index.html
Create a directory named templates in your project directory, and inside it, create a file named index.html. This file will contain the HTML for our web interface:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>PDF to MP3 Converter</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/style.css">
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.6.0.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>PDF to MP3 Converter</h1>
<form id="uploadForm" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="pdf_file" id="pdf_file" accept="application/pdf">
<button type="submit">Upload and Convert</button>
</form>
<div id="status" style="display:none;">
<p id="progress">Converting...</p>
<progress id="progressBar" value="0" max="100"></progress>
</div>
<div id="downloadLink" style="display:none;">
<a id="downloadAnchor" href="" target="_blank">Download Audio</a>
</div>
<script>
$(document).ready(function(){
$('#uploadForm').submit(function(event){
event.preventDefault();
var formData = new FormData(this);
$('#status').show();
$('#progress').text('Uploading PDF...');
$('#progressBar').val(0);
$.ajax({
url: '/',
type: 'POST',
data: formData,
processData: false,
contentType: false,
success: function(data){
if(data.status === 'done'){
$('#progress').text('Conversion complete!');
$('#progressBar').val(100);
$('#downloadAnchor').attr('href', data.download_url);
$('#downloadLink').show();
} else {
$('#progress').text('Converting PDF to MP3...');
checkStatus();
}
},
error: function(){
alert('Error uploading file.');
}
});
});
function checkStatus() {
$.ajax({
url: '/status',
type: 'GET',
success: function(data){
if(data.status === 'processing'){
$('#progress').text('Processing chunk ' + data.current_chunk + ' of ' + data.total_chunks);
$('#progressBar').val((data.current_chunk / data.total_chunks) * 100);
setTimeout(checkStatus, 1000);
} else if(data.status === 'done'){
$('#progress').text('Conversion complete!');
$('#progressBar').val(100);
$('#downloadAnchor').attr('href', data.download_url);
$('#downloadLink').show();
}
},
error: function(){
alert('Error checking status.');
}
});
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
Adding CSS Styles
Create a directory named static in your project directory, and inside it, create a file named style.css. This file will contain our CSS styles:
static/style.css
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
text-align: center;
margin-top: 50px;
}
form {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
#status {
margin-top: 20px;
}
#downloadLink {
margin-top: 20px;
}
Running the Application of PDF-to-Audio Converter
Now that we have all the necessary files, let’s run our Flask application. In your terminal, navigate to your project directory and run:
python app.py
Open your web browser and go to http://127.0.0.1:5000/. You should see the web interface for uploading a PDF file.
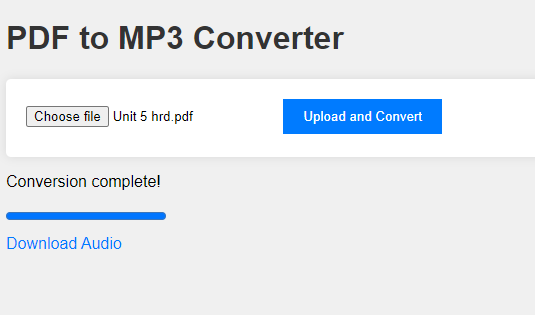
Uploading and Converting a PDF
- Select a PDF File: Click on the “Choose File” button and select a PDF file from your computer.
- Upload and Convert: Click on the “Upload and Convert” button to start the conversion process.
- View Progress: The progress bar and status messages will update to show the conversion progress.
- Download the MP3: Once the conversion is complete, a download link will appear. Click on the link to download the MP3 file.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully created a PDF-to-Audio converter using Python. This project demonstrates how to integrate various Python libraries to build a useful tool. By combining Flask for the web interface, PyMuPDF for reading PDFs, and gTTS for text-to-speech conversion, we created a perfect user experience for converting PDF files to MP3.
Feel free to expand this project by adding features like language selection for the text-to-speech conversion or supporting more file formats.
Source Code for PDF-to-Audio Converter
As I have already provided the complete index.html and styles.css files, here is the full app.py file.
app.py
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, send_file, jsonify
import os
import fitz # PyMuPDF
from gtts import gTTS # Google Text-to-Speech
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import threading
app = Flask(__name__)
app.secret_key = (Your Secret Key) # Replace this with your own secret key
status = {
"current_chunk": 0,
"total_chunks": 0,
"status": "idle"
}
# Lock for thread-safe status updates
status_lock = threading.Lock()
# Function to convert PDF to text using PyMuPDF (fitz)
def pdf_to_text(pdf_file):
text = ""
try:
doc = fitz.open(pdf_file)
for page_num in range(len(doc)):
page = doc.load_page(page_num)
text += page.get_text()
doc.close()
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error reading PDF: {e}")
return None
return text
# Function to convert a chunk of text to MP3 using Google Text-to-Speech (gTTS)
def text_to_mp3_chunk(chunk, chunk_index, output_directory):
try:
tts = gTTS(text=chunk, lang='en')
temp_chunk_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f'chunk_{chunk_index}.mp3')
tts.save(temp_chunk_path)
print(f"Saved chunk {chunk_index} to {temp_chunk_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error converting chunk {chunk_index} to MP3: {e}")
# Function to combine multiple MP3 chunks into a single MP3 file
def combine_mp3_chunks(chunk_count, output_directory, final_mp3_path):
try:
with open(final_mp3_path, 'wb') as final_mp3_file:
for i in range(chunk_count):
chunk_path = os.path.join(output_directory, f'chunk_{i}.mp3')
with open(chunk_path, 'rb') as chunk_file:
final_mp3_file.write(chunk_file.read())
os.remove(chunk_path) # Clean up chunk file
print(f"MP3 saved to {final_mp3_path}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error combining MP3 chunks: {e}")
def update_status(current, total, state):
with status_lock:
status["current_chunk"] = current
status["total_chunks"] = total
status["status"] = state
# Route for the home page
@app.route('/', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def index():
if request.method == 'POST':
pdf_file = request.files['pdf_file']
if pdf_file.filename == '':
return "No file chosen"
mp3_output_directory = './uploads'
if not os.path.exists(mp3_output_directory):
os.makedirs(mp3_output_directory)
if pdf_file and pdf_file.filename.endswith('.pdf'):
try:
# Save the uploaded PDF file
pdf_path = os.path.join(mp3_output_directory, pdf_file.filename)
pdf_file.save(pdf_path)
print(f"PDF saved to {pdf_path}")
# Convert PDF to text
text = pdf_to_text(pdf_path)
if text:
print(f"Extracted text: {text[:500]}...") # Print first 500 characters for verification
# Convert text to MP3
mp3_filename = f"{os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(pdf_path))[0]}.mp3"
mp3_path = os.path.join(mp3_output_directory, mp3_filename)
print(f"Converting text to MP3 and saving to {mp3_path}...")
# Splitting the text into chunks
text_chunks = [text[i:i + 1000] for i in range(0, len(text), 1000)]
update_status(0, len(text_chunks), 'processing')
# Process chunks in parallel using ThreadPoolExecutor
with ThreadPoolExecutor() as executor:
futures = [executor.submit(text_to_mp3_chunk, chunk, i, mp3_output_directory) for i, chunk in enumerate(text_chunks)]
for i, future in enumerate(futures):
future.result() # Ensure each thread completes
update_status(i + 1, len(text_chunks), 'processing')
# Combine all chunks into a single MP3 file
combine_mp3_chunks(len(text_chunks), mp3_output_directory, mp3_path)
update_status(len(text_chunks), len(text_chunks), 'done')
return jsonify({"status": "done", "download_url": f"/download/{mp3_filename}"})
else:
print("Error converting PDF to text.")
return "Error converting PDF to text. Please try again."
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing PDF: {e}")
return "Error processing PDF. Please try again."
return render_template('index.html')
# Route to get the current status
@app.route('/status', methods=['GET'])
def get_status():
with status_lock:
return jsonify(status)
# Route to download the generated MP3 file
@app.route('/download/<filename>')
def download(filename):
mp3_file_path = os.path.join('./uploads', filename)
try:
print(f"Attempting to send file: {mp3_file_path}")
return send_file(mp3_file_path, as_attachment=True)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error sending file: {e}")
return "Error sending file. Please try again."
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
External Resources on PDF-to-Audio Converter
- Flask Documentation: Comprehensive guide for building web applications with Flask.
- PyMuPDF Documentation: Official documentation for PyMuPDF.
- gTTS Documentation: Official documentation for Google Text-to-Speech.
- Real Python: Tutorials and resources on Python programming.
- JavaScript Guide on MDN: Basics of JavaScript.
Frequently Asked Questions – PDF-to-Audio Converter
pip install Flask
pip install PyMuPDF
pip install gTTS



Leave a Reply